Vitamins and minerals play an important role in our growth and development. If any of the vitamins are deficient, we may develop a deficiency disease which might cause permanent harm to our bodies. Â Besides providing essential nutrients to maintain healthy cells in our bodies, vitamins may also be used to prevent or, to some extent, reverse the damages cause by gingivitis.
Vitamins and minerals play an important role in our growth and development. If any of the vitamins are deficient, we may develop a deficiency disease which might cause permanent harm to our bodies. Â Besides providing essential nutrients to maintain healthy cells in our bodies, vitamins may also be used to prevent or, to some extent, reverse the damages cause by gingivitis.
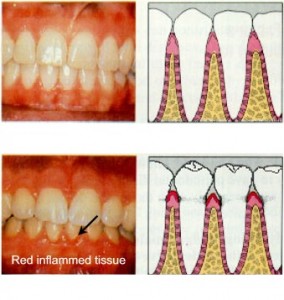
What is gingivitis?
Gingivitis is the term used for the inflammation of gum tissues, a non-destructive from of periodontal disease. It is perhaps the most common human disease as chronic gingivitis can be seen in most of the population in the world, and is among the easiest to treat and control. In absence of treatment, gingivitis may progress to the destructive form of periodontal disease, periodontitis.
You may be having gingivitis if you have the following symptoms:
- tender, swollen, or red gums
- bleeding gums while brushing or flossing
- bad breath in some cases
Causes of gingivitis
Plaque-induced gingivitis is the more common form of the disease and it mostly begins as an inflammation caused by an accumulation of bacterial plaque adhering to teeth, to tartar (calculus) and to fixed and removable fillings or prostheses. Dental plaque is mostly retained in the mouth due to:
- Poor toothbrushing technique
- Irregular shape and placing of the teeth, providing stagnation areas
- Fillings or appliances that cause stagnation areas
Gingivitis can also be caused by systemic factors which include:
- Pregnancy
- Down’s syndrome
- Poorly-controlled diabetes mellitus
Is gingivitis curable?
It is important to recognize the early signs and symptoms of gingivitis for with good oral hygiene practices, a plaque-induced gingivitis of bacterial origin can be cured with gum tissues returning to normal. However, it is usually not possible for the affected tissues to return to normal in periodontitis. Therefore immediate treatment should be given as soon as the gingivitis symptoms and signs are detected to arrest and control the progression of the disease.
How to treat gingivitis?
The best method to treat gingivitis is to physically remove dental plaque so proper oral hygiene regimen is important to clear bacterial plaque adhering to teeth, to tartar (calculus) and to fixed and removable fillings or prostheses. However there are certain areas that are hard to reach with normal toothbrushing, for example deep gum pockets or behind the most posterior molars, and require professional scaling or removal of dental plaque by your dentist.
Mechanical removal of dental plaque and good oral hygiene would be sufficient to cure gingivitis but depending in the severity of the disease; your dentist may prescribe you chlorhexidine mouthwash or in extreme cases, undergo surgery to correct the damages done by the disease.
Which vitamins and minerals are essential for curing gingivitis and reversing its damage?
 It is well understood that a healthy and balanced diet can help prevent many diseases. An inadequate diet may be responsible for unhealthy, inflamed gums. Gum diseases can be prevented or reversed with the help of certain vitamins and minerals.
It is well understood that a healthy and balanced diet can help prevent many diseases. An inadequate diet may be responsible for unhealthy, inflamed gums. Gum diseases can be prevented or reversed with the help of certain vitamins and minerals.
- Vitamin A – help in maintenance of healthy mucous membrane and maintain salivary flow in the mouth.
Food source: Present only in animal foods; beef liver is an excellent source. Beta carotene: carrots, melon, squash, sweet potato, spinach
- Vitamin E – help in healing and restoration of damaged gum tissues.
Food source: Vegetable seed oils, widely distributed in foods.
- Vitamin C – prevents all forms of inflammation of the gums. Deficiency can lead to scurvy and poor wound healing.
Food source: Citrus fruits, papaya, broccoli, potato, strawberries.
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin) – reduction in symptoms of gingivitis.
Food source: Tuna, beef liver, chicken breast, mushroom.
- Calcium – reduce symptoms of gingivitis and help heal and restore damaged bone tissues.
Food source: Milk and milk products, sardines, clams, turnip and mustard greens, broccoli.
- Coenzyme Q10 – help in healing of gums and reversal of gum inflammation.
Food source: Meat, fish; beef, pork, chicken liver and heart; vegetable oils, parsley.
- Zinc – help improve immune system and bones.
Food source: Wheat germ, oysters, beef liver, dark meat of poultry. Abnormal taste and smell
How to prevent gingivitis?
Early detection and treatment of gingivitis can help prevent the disease progression to periodontitis. Therefore it is best to:
- Practice good oral hygiene with proper tooth brushing techniques and the usage of floss and mouthwash
- Make regular appointments with your dentist to ensure your mouth stays in a healthy condition by having professional cleaning of the teeth every 6 months or as recommended by your dentist
- Maintain good general health by having proper nutrition and exercise
- Stop smoking