Parents or guardians play an important role in regard to a child’s diet and oral health habits. Newly emerged teeth are particularly vulnerable to dental decay. As teeth gets older and become more mature, the outer surface becomes harder and more resistant to acid attack.
Teeth are constantly being attacked by acid produced by plaque bacteria as well as acidic foods and drinks. Acids cause damage below the tooth surface, causing microscopic holes in the tooth. If the acid damage continues over a period of time, the tooth becomes so fragile that a hole becomes visible in the tooth. As the hole gets bigger, the tooth will need a filling. However dental sealants can be placed on your child’s teeth to prevent tooth decay from occurring if risk of decay is detected early.
What are dental sealants?
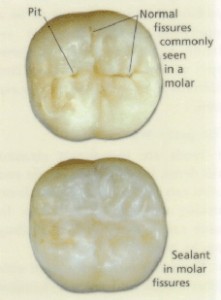
A dental sealant (or fissure sealant) is a professionally applied clear or tooth-colored protective coating made of a resin which is similar to that used in some of the tooth-colored fillings. It protects the deep grooves on the back teeth which are hard to clean because the toothbrush bristles are too thick to fit into the grooves or fissures of the teeth, allowing plaque to get trapped and create cavities.
The procedure is similar though less complicated than for white fillings. Placement of the sealants is not time consuming and it is a painless procedure that usually requires no injections and drilling. The tooth surface has to be thoroughly cleaned and kept completely dry while the coating is put in place. Special equipment or lots of cotton rolls may be used to keep saliva away from the tooth.
Once placed, a strong light may be used to set the protective coating. Your child can eat on the finished sealant straight afterwards. Dental tooth sealant lasts on average two to seven years and dental sealant program is available as required/recommended through the School Dental Service.
What are dental fillings?
A dental filling is a professionally placed dental restorative material on a tooth which has lost its original structure due to decay or trauma. It is used to restore the function, integrity and shape of the missing tooth structure.
Placement of dental fillings may take time depending on the amount of tooth structure that needs to be replaced. It usually involves removal of additional tooth structure by drilling during tooth preparation to improve the aesthetics or the support of the intended restorative material. Sometimes injections may be required if the decay or trauma runs deep.
Why sealants may be recommended for some teeth
During each visit your dental professional will assess your child’s risk of decay. If teeth are considered to be at risk, dental sealants prevent dental caries in children with tooth surfaces that are most likely to develop cavities. Sealants will stop the need for fillings later on but do note that sealants will not last forever. Regular dental check-ups are essential to ensure that dental sealants are still fully covering the risk area, otherwise decay may occur. If even part of the protective coat is lost, the tooth will be at risk again.
When are sealants indicated?
Fissure sealants will more likely be needed when:
- There are narrow grooves and fissures on newly erupted permanent back teeth (molar)
- There are staining on the grooves and fissures
- There is decay in one of the first permanent molar and the rest of the healthy molars should be sealed
- Your child has special needs
- There is extensive tooth decay in the baby teeth
Are sealants really necessary?
 The four pillars to tooth decay prevention are toothbrushing, diet, fluoride and fissure sealants though teeth sealants are not needed if your child can stop decay from occurring. This may require changes in eating and brushing habits.
The four pillars to tooth decay prevention are toothbrushing, diet, fluoride and fissure sealants though teeth sealants are not needed if your child can stop decay from occurring. This may require changes in eating and brushing habits.
- Limit sugar and refined carbohydrates products in your food and drinks
- Effective brushing with fluoride toothpaste morning and night
- Cut down on sweet snacks and sweetened drinks especially before bedtime
If decay is beginning to develop, your dental professional may suggest that sealants be placed over the back teeth that are still healthy to protect them from acid attack and reduce the need for fillings at a later date. Once a tooth has a filling, it is not as strong as an unfilled tooth and it will have a greater risk of developing further decay.
Your dental professional will try to help you keep your teeth free of fillings to ensure that you have healthy teeth throughout your life therefore make it a habit to visit your dental professional at least every six months.