What are gums?
Gums are also known as gingival. They are part of oral tissues which support our teeth and cover the bone. Â 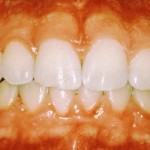
What do healthy gums look like?
Healthy gums are pink in color (gingival color varies based on racial pigmentation), firm, stippled (orange peel) in texture and scalloped to the contour of teeth.
Why do my gums bleed when I brush my teeth?
Most people think that it is normal to have bleeding gums during brushing, but it is a sign that your gums are inflamed. Actions should be taken to improve your oral hygiene or visit a dentist to have professional cleaning done.
What are the causes of gum disease?
Bacteria irritation (highly found in dental plaque) is the main cause of periodontal disease. Besides that, local factors such as malaligned teeth, denture and orthodontic appliances, faulty fillings are highly plaque accumulative. Smoking is also a factor that contributes to periodontal disease. Click here to read more on smoking and its effects on periodontal tissues. http://www.intelligentdental.com/2011/07/18/dental-health-and-smoking/
Can hormones affect gums?
The two main female sex hormones, oestrogens and progesterone can affect our gums by increasing the severity of existing gum disease and  the permeability of gingival blood vessels. This condition is exhibited especially during puberty, pregnancy and during the use of oral contraceptive.  Thus, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene as small amount of dental plaque can cause gingival inflammation.
What are the signs and symptoms of gum diseases?
In early gum disease/ gingivitis: There will be: 1.      Altered gingival appearance Unhealthy gums may appear swollen and reddish due to underlying inflammation. 2.      Gums can bleed easily when provoked during brushing or eating hard food. 3.      Bad breath.  In later stage, where bone loss and deep pockets occur,(Chronic periodontitis)  Signs and symptoms that you will face: 1.      History of bleeding gums 2.      Formation of pockets (our gums are separated from tooth surface) The severity of periodontal disease can be measured by placing a dental probe into your gingival “pocketâ€. A measurement of 4mm indicates an early chronic periodontitis. Diagnosis of chronic periodontitis is also confirmed by looking at your bone level through radiographic evidence. 3.      Teeth are mobile (due to loss of bone) 4.      Bad breath/ halitosis
Â
What are the treatments for early gingivitis?
1.      Seek professional scaling to remove plaque and calculus.
2.      Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly.
3.      Correction of plaque retention factors such as replacing faulty fillings and etc
Â
What will the dentist do if I am diagnosed with chronic periodontitis?
1.      Scaling and root planning.
Root planning is done by introducing an instrument into your pocket and remove the necrotic cementum and embedded calculus. 2.      Periodontal surgery based on the severity of your condition.
What can I do to improve my gingival health?
The best solution to improve your gingival health is to maintain a good oral hygiene and keep our teeth and gums free from bacteria irritation. Below are some tips to improve your gingival health:
1.      Brush and floss effectively.
2. Â Â Â Use interdental brush to remove plaque interdentally and near to gingival crevice.
3. Â Â Â Â Use mouthwash for its antibacterial effect.
4. Â Â Â Stop smoking as it worsen your gums condition.
5. Â Â Â Visit your dentist regularly for professional scaling.