Recent advances in diagnostic methods
1. RADIOVISIOGRAPHY
2. XERO – RADIOGRAPHY-
3. PULSE-OXIMETRY:
4. LASER DOPPLER FLOWMETRY
5. COMPUTERISED TOMOGRAPHY
6. DIGITAL SUBTRACTION RADIOGRAPHY
7. MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
8. COMPUTERISED EXPERT SYSTEM.
9. THERMOGRAPHIC IMAGING.
10. TACT:( TUNED APERTURE COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY)
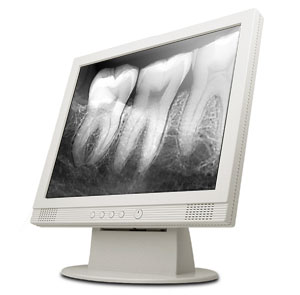
1.RADIOVISIOGRAPHY
R.V.G digitizes ionizing radiation and provides an instantaneous image on a video monitor thereby reducing radiation exposure by 80% R.V.G equipment has a fiber optic intra oral sensor (with a selenium coated plate).
Advantages
1.Elimination of X-ray film.
2. Significant reduction in exposure time
3. Instantaneous image display.
The R.V.G. has 3 components:
The “ RADIO†component X-ray unit.
The “VISIO†portionâ€
The “GRAPHYâ€component.
a) The “RADIO†component-consists of a hypersensitive intra-oral sensor and a conventional x-ray unit.
b) The “VISIO†portion –consists of video monitor and display processing unit.
c) The “GRAPHY†component- is a high resolution video printer that instantly provides a hard copy of the screen image using the same video signal.
the R.V.G. system appears to be promising for the future of Endodontics. But the resolution of R.V.G. is slightly lower than that produced with conventional films, which can however be improved through enhancement procedures.
2.XERO – RADIOGRAPHY
The term Xero-radiography is derived from the Greek word XEROS which literally means dry which differentiates X’ radiography from the conventional photochemical system.
Technique:
X’ radiography uses a rigid aluminum / selenium coated photoreceptor plate. The plate is electrically charged, placed in a water proof electric cassette, positioned in the mouth and exposed to X–rays at a lower level of radiation. The entire process requires only 25 seconds for a dry permanent image. The plates may be reconditioned, recharged and used repeatedly.
Advantages:
It produces sharper, clearer and finer details of the image.
Reduced radiation dose is required.
Pronounced edge enhancement is observed.
3. PULSE-OXIMETRY:
Tests relying on the passage of light through a tooth have been considered as a possible means of detecting pulp vitality with greater objectivity.
Pulse oximetry is a relatively recent advancement in non-invasive monitoring. It is a non-invasive oxygen saturation monitor that also provides continuous pulse rate readings.
The liquid crystal display (L.C.D)
Gives Oxygen saturation pulse Rate(and plethysmographic wave from readings)
Concept: Pulse oximetry uses red and infrared wave lengths in order to transilluminate a tissue and detects absorbance peaks due to pulsative circulation and uses this information to calculate the pulse rate and oxygen saturation
The tooth being tested is sandwiched between a photoelectric detector and an L.E.D (light emitting diodes) of red and infrared lights.
This method is clearly superior to other vitality testing methods, since it does not rely on sensory nerve response.
4. LASER DOPPLER FLOWMETRY:
Due to the biased, false negative and positive response elicited through the E.P.T, the need for a better and more reliable method for determining the pulp vitality arose. A method, which determined and registered the blood flow rather than the neural response was preferred.
The crux of the L.D.F. is based on the detection of movement of blood cells in the pulpal blood vessels (and not on neural responses) which thus gives a truer picture regarding pulp vitality.
The technique-essentially consists of a laser at 632.8 nm and is focused on the tissue study with a fiber optic probe. As the light hits various components of the tissues it is partially absorbed and partially back scattered.
The back-scattered light has 2 components:
1. Light back-scattered from static tissues which has the same frequency as the light going in.
2. The other component is the DOPPLER shifted light with a different frequency
The back scattered light is processed and an output signal is produced i.e. both the unshifted and shifted light is transmitted to a detector by optical fibers where it is converted into electric current and processed.
The detected output signal can be fed into an analog printer,
or be read from a digital board
Advantages of L.D.F:
Non invasive
Simple to apply
Provides a continuous record
Useful to demonstrate establishment of vitality of untreated teeth
Disadvantages
Impossible to calibrate the readings in absolute units.
Output may not be linearly related to blood flow
5. COMPUTERISED TOMOGRAPHY
C.T. is a radiographic technique that blends the concepts of thin laser radiography with the computed image
Techibana has reported about the use of C.T in endodontics.It is possible to determine the bucco-lingual and mesio-distal widths of teeth and the presence or absence of root canal filling materials and metal posts. Also observable are the carious lesions, extension of the maxillary sinus and its proximity to the root apices
Advantages
Observation of structures, which are difficult to visualize with conventional X-ray
Provides images for 3- D reconstruction of roots, root canals and teeth
Disadvantages
1.Expensive
2.Skin dose is large
3.Time Consuming
6 .DIGITAL SUBTRACTION RADIOGRAPHY:
The progress of caries from an incipient lesion, through the DEJ is often difficult to detect. Likewise the assessment of healing or expansion of the periapical lesion after R.C. therapy is a challenge because the subtle changes in the density of the lesion may not be detectable with the naked eye
Subtraction radiography offers a remedy for these problems.This is an image enhancement method,
Resulting in the area under focus being clearly displayed against a neutral gray black background or it is super imposed on the radiography itself i.e, required areas are enlarged against the entire background
This D.S.R may be used to asses the successfulness of R.C.T and also periapical lesions.
7.MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
Recently MRI has been tried out as a diagnostic tool in Endodontics. Magnetic fields and radiographic waves are used to generate high quality cross sectional images of the body. M.R.I can distinguish blood vessels and nerves from surrounding soft tissues.
However, this needs very large equipment. the high electromagnetic waves which are needed have not been approved of for use in scanners. it is believed that MRI machines will be developed for evaluation of odontogenic problems
Disadvantages: Not to be used in patients with cardiac pace makers, metallic restoration / ortho appliances,
COMPUTERISED EXPERT SYSTEM.
Appropriate diagnostic facts are obtained and this data is entered into the computer. The computer checks gives out the diagnosis. with rapid advances being made in the field of computers, we may get many more programmes for efficient endodontic diagnosis.
9. THERMOGRAPHIC IMAGING.
10. TACT:( Tuned aperture computed tomography)
