Inserting a foreign body into our body may bring risk of complications. The same goes for injecting local anesthetic agents or pain numbing solution into the mouth for a dental procedure. Complications in administrating dental anesthesia may occur due to preventable or unpreventable circumstances.
What is local anesthesia?
Local anesthesia has been defined as a loss of sensation in a specific area of the body without inducing a loss of consciousness. Local anesthesia s normally provided through topical application or by needle injection if the dental procedure require so.
What are the complications that can happen in local anesthesia?
Complications in local anesthesia can be categorized into local and systemic complications.
Local complications
Needle breakage
Rare since the use of disposable needles. Smaller (30- and 27-gauge) needles are more likely to break than larger (25-gauge) needles.
Causes:
- weakening of the dental needle by bending it,
- sudden unexpected movement of the individual especially children
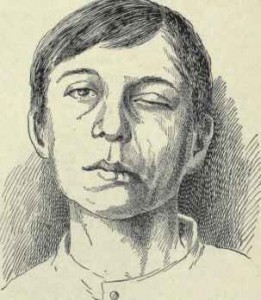
Facial nerve paralysis
Terminal branches of facial nerve may be injured during administration of local block anesthesia near the region. The face on one side will be lopsided and there is inability to blink one’s eye.
Persistent anesthesia or paraesthesia
Sometimes can last for more than a few hours. At times it may persist for days, weeks or months; yet it is an unpreventable complication.
Causes:
- local anesthesia contaminated by alcohol or sterilizing solution that results in swelling and increased pressure in nerve region,
- trauma to nerve covering by needle,
- bleeding into or around neural covering,
- concentration of local anesthesia particularly 4%
Trismus
Trismus is the prolonged titanic spasm of the jaw muscles by which the normal opening of mouth is restricted
Causes:
- if alcohol or cold sterilizing agents have been diffused it can cause prolonged trismus,
- local anesthesia if injected in muscle can cause necrosis of that part of the muscle,
- large volumes of bleeding can cause tissue irritation leading to muscle dysfunction,
- a low grade infection can also cause trismus,
- extensive deposition of local anesthetic volumes can cause distention of tissues leading to post-operative trismus
Soft tissue injury
More frequent in children as soft tissue anesthesia lasts longer than tooth pulp anesthesia.
Hematoma
A localized swelling filled with blood can occur while inadvertently nicking a blood vessel. Hematoma can result in pain or trismus.
Pain on injection
Causes:
- careless attitude of administrator,
- dull needle due to multiple injections,
- rapid deposition of local anesthetic solution,
- needles with barbs
Burning on injection
Causes:
- depends on acidity of the anesthetic solution,
- rapid injection technique,
- contamination of solution by alcohol and other sterilizing solution,
- very warm solution
Infection
Rare after introduction of cartridges
Edema or swelling
Causes:
- trauma during injection,
- infection,
- allergy,
- bleeding,
- hereditary angioedema
Sloughing of tissues
Prolonged irritation or ischemia can cause shedding of skin cells or sterile abscess
Pre-anesthetic intraoral lesions
Apthous ulcers, herpes simplex
Systemic complications
Adverse reactions can occur due to:
- Toxicity caused by direct extension of the usual pharmacological effects of the drugs
- side effects,
- overdose reactions,
- local toxic effects
- Toxicity caused by alteration in the recipient of the drug
- a disease process like liver or kidney failure, congestive heart failure;
- emotional disturbances;
- genetic disease (atypical plasma pseudocholinesterase)
- Toxicity caused by allergic response to drug
Overdose reactions
The most common of all the adverse reactions, it is defined as overly high level of the drug in the body. Toxic doses can lead to seizures.
Predisposing factors
Individual factors – age, weight, other drugs (phenytoin, desipramine), gender, presence of disease, genetics, mental attitude
Drug factors – capacity of blood vessels expansion, concentration, dose, route of administration, rate of injection, vascularity of the injection site, presence of vasoconstrictors
Pre-convulsive signs and symptoms of central nervous system toxicity
Signs – tremor of muscles of face and hands or legs, generalized lightheadedness, dizziness, visual disturbances with inability to focus, tinnitus, drowsiness, disorientation
Symptoms – slurred speech, numbness of tongue and surrounding region, shivering, warm, flushed feeling o skin, muscular twitching, pleasant dreamlike state
Most of the serious overdose reactions have occurred in children – usually the well-behaved two to six years olds less than 40kg.
Causes:
- often treated on all four quadrants of the mouth at the same appointment,
- usually plain local anesthetic administered,
- exceeding maximum dose based on child’s weight
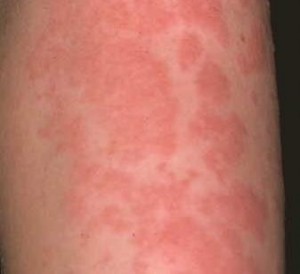
Allergy
Allergic responses include dermatitis (inflammation of the skin – most common), bronchospasm (asthmatic episode) and systemic anaphylaxis. Nowadays local anesthesia comes without the preservatives and bacteriostatic agent methyl paraben. Another potential allergic agent is sodium bisulfite (anti-oxidant). Latex allergy can also occur from the thick rubber plunger.
Signs and symptoms of allergic reactions
- Skin itching, rash, swelling,
- cramping, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,
- angioedema, expansion of blood vessels, decrease in blood pressure
If there is anything else more than the above, then it is likely to be an overdose reaction.