Wound closure techniques have evolved from the earliest development of suturing materials to comprise resources that include synthetic sutures, absorbables, staples, tapes, and adhesive compounds. The engineering of sutures in synthetic material along with standardization of traditional materials (eg, catgut, silk) has made for superior aesthetic results. Similarly, the creation of natural glues, surgical staples, and tapes to substitute for sutures has supplemented the armamentarium of wound closure techniques. Aesthetic closure is based on knowledge of healing mechanisms and skin anatomy, as well as an appreciation of suture material and closure technique. Choosing the proper materials and wound closure technique ensures optimal healing. Continue reading
Tag Archives: Inflammation
Bald tongue
A smooth tongue is also known as Atrophic glossitis, bald tongue or Moeller glossitis. ‘Atrophic glossitis‘ is a condition where one’s tongue turns a different shade of color, swelling in the process. The inflammation is brought on due to many factors, which we will look into later. Small protruding vertical structures, called papillae, are not present anymore, giving the tongue a smooth and bald look. Due to this problem, one can have difficulty eating, and taking in air, as this starts to block one’s airway. We find out what is behind this problem, and how it can be treated upon examination. Continue reading
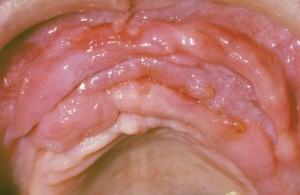
Desquamative gingivitis
Desquamative gingivitis is a cutaneous condition characterized by diffuse gingival erythema with varying degrees of mucosal sloughing and erosion.
A band of red atrophic or eroded mucosa affecting the attached gingiva is known as dequamative gingivitis. Unlike plaque-induced inflammation it is a dusky red colour and extends beyond the marginal gingiva, often to the full width of the attached gingiva and sometimes onto the alveolar mucosa. DG is more common in middle-aged to elderly females, is painful, affects the buccal/labial gingiva predominantly. Some reserve the term for cases where the epithelium blisters or peels while others use it whenever the characteristic red appearance is present. (Edward W. Odell, 2010) Continue reading
Bell’s palsy Part 2
Pathology
It is thought that as a result of inflammation of the facial nerve, pressure is produced on the nerve where it exits the skull within its bony canal, blocking the transmission of neural signals or damaging the nerve. Patients with facial palsy for which an underlying cause can be found are not considered to have Bell’s palsy per se. Possible causes include tumor, meningitis, stroke, diabetes mellitus, head trauma and inflammatory diseases of the cranial nerves (sarcoidosis, brucellosis, etc.). In these conditions, the neurologic findings are rarely restricted to the facial nerve. Babies can be born with facial palsy. In a few cases, bilateral facial palsy has been associated with acute HIV infection. Continue reading
The Effects of Lip Rings on Teeth
Piercing is a popular way to decorate the body and enhance features. While the trend is popular, lip piercing does present some problems for the mouth and gums. If you wish to get a piercing, always visit a professional who follows proper sanitary practices. Make sure the piercing and the mouth is cleaned with mouthwash regularly to avoid infection. Good and effective tooth brushing methods must also be establish as it is the fundamental requirement for good oral hygiene. Continue reading
Relationship between Gum Disease and Heart Disease
The number one cause of mortality in the United States since 1900 continues to be heart disease. And gum disease and heart disease appear to be related, thanks to several extensive studies in the early 2000s which suggested that people with gum disease (periodontal disease) were twice as likely to also have coronary artery disease, along with other heart-related health conditions. Both diseases are complex and share some of the same risk factors including smoking, genetics, increasing age and stress. While these studies have not definitively proven that gum disease causes heart disease, they have clearly shown that there is some correlation between the two. The understanding of this relationship and what to do about it is very important.   Continue reading
Common Inflammatory Disease of the Jaw Bone
 Inflammatory Disease of the Bone
Inflammatory Disease of the Bone
Inflammation is a protective tissue response to injury or destruction of tissues, which serves to destroy, dilute, or wall off both the injurious agent and the injured tissues. The classical signs of acute inflammation are pain (dolor), heat (calor), redness (rubor), swelling (tumor), and loss of function (functio laesa). Continue reading
Denture-related problems affecting the mouth Part2
continuation of part 1
4)Â Â Â Â Â Epulis fissuratum (denture fibrous hyperplasia)
Commonly seen in those with poor fitting denture for a long period of time, the lesion may be due to the sharp denture margins or overextended flanges leading to chronic irritation of the soft tissues. It can appear as a single or multiple fold of tissue that grown in excess around the mucobuccal groove, which is the area where the gums meet the inner cheek. The tissue‘s mobility and continued growth can cause problems in maintaining denture retention. Painful ulceration is common in the base of the fold.
Treatment: Surgical excision of lesion and new denture construction. Continue reading