Whenever a lesion is observed on a radiograph, it must first be described in general terms before a differential diagnosis is attempted. Is the lesion radiolucent, radiopaque, or mixed (combination of radiolucency and radiopacity)? Where is the lesion located? The apices of which teeth are involved? What is the size of the lesion? Is the margin of the lesion ill-defined, well-defined, or well-defined with a radiopaque border? Is the appearance of the bone surrounding the lesion: normal, porous, or sclerotic? Continue reading
Tag Archives: pulpitis
Pulp Disease – Part 1
The pulp has been described both as a highly resistant organ and as an organ with little resistance or recuperating ability.
Its resistance depends on cellular activity, nutritional supply, age, and other metabolic and physiologic parameters.
How to Root Canal a Baby Teeth
The purpose of root canal treatment with baby teeth is to keep the teeth in function until exfoliation, or at least for as long as they are important for occlusal development. Besides eating and speaking, many parents do not know that baby teeth (or primary teeth) also act as a guide for the underlying permanent teeth to erupt and at the same time they maintain the space on the arch so that the permanent teeth has enough room to grow when it is out. Continue reading
Symptoms indicating when you need a Root Canal Treatment
What is Root Canal Treatment (RCT)?
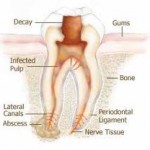 Root canal treatment is the removal of inflamed and/or infected dental pulp tissue from the root canal system, shaping and filling the root canals of a diseased tooth. The key factor in the development of pulpal inflammation and breakdown of the supporting tissues of the tooth (periradicular tissues) is the presence of bacteria. These endodontal infections (infections within teeth) are usually characterized by loss of integrity of the crown, invasion by bacteria, and destruction of enamel, dentine, and eventual pulpal involvement. Dental caries, trauma, tooth surface loss, and microleakage around tooth fillings can lead to endodontal infection. In situations where there has been periradicular breakdown, root canal treatment will result in the return of the health of the periradicular tissues. Ultimately, root canal treatment preserves teeth as functional units within the dental arch. Continue reading
Root canal treatment is the removal of inflamed and/or infected dental pulp tissue from the root canal system, shaping and filling the root canals of a diseased tooth. The key factor in the development of pulpal inflammation and breakdown of the supporting tissues of the tooth (periradicular tissues) is the presence of bacteria. These endodontal infections (infections within teeth) are usually characterized by loss of integrity of the crown, invasion by bacteria, and destruction of enamel, dentine, and eventual pulpal involvement. Dental caries, trauma, tooth surface loss, and microleakage around tooth fillings can lead to endodontal infection. In situations where there has been periradicular breakdown, root canal treatment will result in the return of the health of the periradicular tissues. Ultimately, root canal treatment preserves teeth as functional units within the dental arch. Continue reading