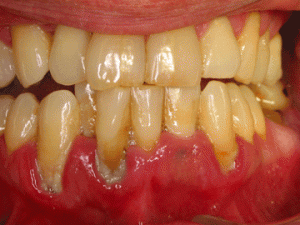
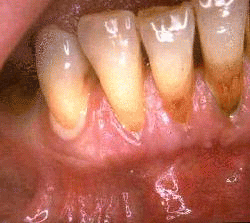
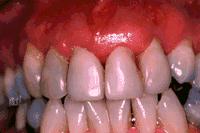
Periradicular, periapical or apical periodontitis can be defined as inflammation of all the supporting structures of the teeth in the area surrounding the apex of the tooth. Periapical inflammation is usually due to tooth infection which characteristically causes pain of tooth in its socket. It is often accompanied by destruction of bone and occasionally, the root apex of tooth. However the periapical tissue has the ability to heal if the cause of inflammation is removed. Periapical periodontitis can be divided into acute and chronic apical periodontitis. Continue reading