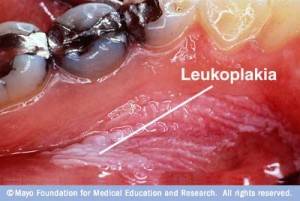
Lesion seen on the floor of the mouth

Lesion seen on the floor of the mouth
Definition of Oral Leukoplakia:
Oral Leukoplakia is a white lesion (abnormal tissue) found on the oral mucosa (skin lining in our mouth).It has no known causing agents. For example, a thrush lesion in the mouth is also white , but it is not an Oral Leukoplakia lesion because it is proven to be caused by the candida fungus.
Sign and symptoms of Oral Leukoplakia:
- Leukoplakia size can vary from a small ,well rounded plaque (broad, raised area on the skin) to a large and extensive mucosa lesion(any abnormal tissue found on or in an organism)
- Leukoplakia color may be white, whitish-yellow or grey .
- Homogeneous Leukoplakia has an even distributed surface which is smooth, wrinkled or criss-crossed by small cracks or fissures.
- Non-Homogeneous Leukoplakia has an uneven surface which is usually reddish and ulcerated or warty.
- Speckled Leukoplakia or erythroluekoplakia (leukoplakia with reddish spots) usually develops from a uniform white lesion and progresses to become red and ulcerated. This change in features usually indicates a cancerous Oral Leukoplakia.
Treatment of Oral Leukoplakia:
Treatment of Oral Leukoplakia is very subjective:
If the white lesion is found to be non–cancerous, then the best treatment would be to remove or try to eliminate the above predisposing factors. Then, leave the white lesion alone and continue close observation by the dentist.
If however the white lesion is found to be cancerous , the best treatment would be to surgically remove the white lesion, undergo radio and chemotherapy to control the spread and malignancy.
Causes of Oral Leukoplakia:
There are no known definite causes; however these are the possible predisposing factors:
- Smoking or chewing tobacco. The irritation from the chemicals in the tobacco is considered to be the number one contributing factor. White lesions here are usually seen on the cheeks, lips or tongue.
- Sunlight or UV light exposure.
- Chronic irritation from foreign materials or objects in the mouth.
- Predominantly seen in chronic drinkers.
- Human papilloma viruses (HPV) are commonly detected in Oral Leukoplakia. Note that HPV virus’s type 16 and 18 are high risk types due to their association with cancer of the cervix. “Hairy Leukoplakia” is sometimes seen in immune compromised patients, but are not categorized under Oral Leukoplakia due to the fact that it has a known cause which is the Ebstein-Bar virus.
- Oral epithelial atrophy (wasting away). Conditions which predispose to atrophy are iron deficiency, tertiary syphilis, oral sub mucosa fibrosis.
- Mutation of p53 a tumor suppressor gene can result in uncontrolled cell divisions leading to abnormal oral mucosa growth of Oral Leukoplakia.
Test and Diagnosis of Oral Leukoplakia:
The Diagnosis of Oral Leukoplakia can only be accomplished by eliminating the possibilities of other diseases.Therefore, the diagnosis is not based mainly on a specific cellular arrangement seen under the microscope, but a diagnosis is made based on what the clinician sees at chair side.
However, if the diagnosis does point to Oral Leukoplakia, the next step is to obtain a tissue sample from the white lesion. The tissue sample is than sent to a lab to study the amount of dysplasia (abnormal growth of cells) seen in the tissue sample. The amount of dysplasia can usually tell us if the lesion is a cancerous Oral Leukoplakia.
Prognosis of Oral Leukoplakia:
What is the prognosis of Oral Leukoplakia ? The only real concern here is whether a not this lesion is cancerous. Studies has shown that about 5%-14% of Oral Leukoplakia cases become cancerous. Not all Oral Leukoplakia are cancerous, some are just benign.
Malignancy of Oral Leukoplakia are usually influence by many combining factors, such as smoking, nutritional habits, condition of living, genes and many more. No single factor is responsible.
The area where the white lesion occurs at also plays an important factor. Lesions found on the floor of the mouth or below the tongue are mostly cancerous.
White Lesions which changes in appearance drastically are also an indication of a cancerous lesion. For example, in the case of speckled leukoplakia.
Complications of Oral Leukoplakia:
For non-cancerous lesions, the only complication would be that it is aesthetically displeasing. In cases of cancerous Oral Luekoplakia, the most obvious complication is late detection and spread of the cancerous lesion to other parts of the body. Once the cancerous lesion spreads, it can be fatal.
When to contact a doctor:
You should immediately see a dentist if :
- Any white lesions appears in the mouth and is a persistent condition after 2-3 weeks even after oral aid medication.
- The white lesion suddenly changes in appearance and looks worse.
- White lesion is initally painless and progresses to becomes painful.
- White lesion starts to spread.
Pingback: How to differentiate milk and thrush in a babies mouth | Intelligent Dental
this pic is an example of which type of leukoplakia?