Definition
Lichen planus is a disorder affecting the skin or in the mouth.70% of patients with skin lesions have oral involvement, but only 10% of patients presenting with oral lesions have involvement .It is more common in women over 30-50 years of age.
Types
- Plaque-like
- Reticular
- Papular
- Erosive
- Atropic
- Bullous
Causes
The exact cause of oral lichen planus is unknown. However, it is likely to be related to an allergic or immune reaction. Predisposing factors include:
- Exposure to medications, HIV infection, liver disorders, reaction to amalgam or gold
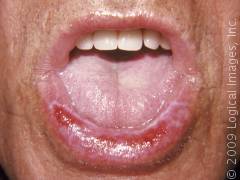
lichen planus tongue
Signs and symptoms of oral lichen planus
- White irregular striae lesions
- Tend to be both sides (bilateral)
- Maybe asymptomatic or sore, especially with hot and spicy foods
- The atropic and erosive varieties though, are often painful
- Lacy, firm adherent, white plaques usually on inside of the cheek
- May also affect sides of tongue, gum and lips
- Painful (mild cases may have no discomfort)
- Lesions occasionally form painful ulcers
Investigations & diagnosis
Biopsy required to confirm diagnosis in cases of doubt and to differentiate from lichenoid reaction, keratosis, systemic lupus erythematosis or other white lesions
Treatment
Asymptomatic: no treatment
Symptomatic: Topical corticosteroid and rarely, intralesionally or systemically
Other drugs such as retinoids, griseofulvin or cyclosporine may have adverse effects.
Prognosis
Oral lichen planus is generally not harmful and can be cure. However it can recur if the predisposing factor is not removed or healed. It may have a small cancer potential
When to contact a doctor
Visit the doctor if:
- Your symptoms continue and get worse
- The skin or oral lesions change in appearance
- The condition recur even after treatment
![Reblog this post [with Zemanta]](http://img.zemanta.com/reblog_e.png?x-id=2186ba78-6f30-435d-9571-beadd652348b)