What is Trench Mouth?
Trench mouth is also known as Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (ANUG) or Vincent’s infection. It is an acute
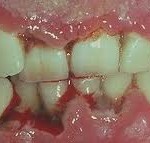
ANUG
 necrotizing inflammatory disease produced by endogenous infection where systemic changes, predispose the gingiva to invasion by bacteria. A recurring periodontal disease which results in necrosis and ulceration of the gums. It is a communicable infection of the respiratory tract and mouth extending to the tongue, palate, throat and pharynx. ANUG is a mixed bacterial infection with predominant groups of anaerobic bacteria, the fusiform, spirochetes and treponema. They present in large numbers in slough and necrotic tissue at surface of the ulcer and invade a small distance into underlying connective tissue, releasing toxins and enzymes. Trench mouth is a serious oral disease which causes severe pain and major discomfort. Inability to carry out good oral hygiene and poor nutritional status are the contributing factors of trench mouth. Other causes include smoking, increased physical and emotional stress, age, poverty and infections like HIV, AIDS and measles, malignant tumors and acute leukemia.
Â
How to Identify Symptoms of Trench Mouth?
Â
Intraoral Signs and Symptoms include:
1 .Severe gum pain, redness and swelling of the gums
2. Fetid odor or halitosis
3. Foul-smelling taste in the mouth
4. Crater-like ulcers between teeth and on the gum line, filled with plaque and food debris.
5. Spontaneous gum bleeding after a slight touch
6. Pain when eating or swallowing
7. Grayish film on the gums caused by decaying gum tissue
8. Pasty saliva/increased salivation
9. Constantly radiating pain that is aggravated by eating spicy or hot foods and chewing
10. Gum tissue may be worn down or completely destroyed
11. Periodontal disease causes teeth to be more sensitive, loose or even fall out
Extraoral Signs and Symptoms present as:
- Mild to moderate fever
- Swollen lymph nodes around the head, neck or jaw due to bacteria
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue and malaise
The onset of symptoms are sudden. Â The first three are the commonly occurring symptoms of trench mouth while others may develop at a later stage. The symptoms may go unrecognized until the disease reaches an advanced stage.
Diagnosing Trench Mouth
Â
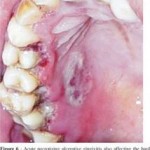
Dentist will perform a thorough clinical examination of your teeth and gums. X-rays may be needed to determine if the infection has caused damage to the gum tissues and bone destruction. Other tests can be done to investigate any underlying immunodeficiency or systemic disease. Pseudomembrane can be differentiated from aphthous ulcers by spraying water over the ulcerated area, pseudomembrane will eventually wash away.
Â
Managing Trench Mouth
Â
With timely treatment and proper oral care, one can recover from trench mouth disease within a couple of weeks. To prevent recurrence, good nutrition is essential in maintaining healthy teeth and gums. Avoid use of tobacco. Administer proper brushing twice daily in the morning and evening before going to bed. Practice regular flossing. Use a mouthwash after every meal to wash away food particles. Imbedded loose food particles can trap bacteria and further spread the existing infection. Essential oils of peppermint, spearmint, almond and clove oil are natural and herbal products having great oral health benefits. You can use them as a mouthwash when mixed with water, rinse and gargle or drop some amount on your toothbrush and brush as usual. They are less abrasive than commercial oral health products available and do not irritate the gums. Warm salt water rinses can also help the gums of those suffering from trench mouth. Hydrogen peroxide rinses releasing oxygen will help to combat the anaerobic bacteria’s activity in the mouth.  All forms of local irritation should be removed such as overhanging filling margins, partially erupted teeth and food impaction. Over the counter medication like ibuprofen can help relieve the pain. Further deep cleaning treatment below the gumline may be needed and include local antibiotic therapies. Drink sufficient liquids, get enough rest and exercise to manage your oral health. Avoid becoming overstressed unnecessarily.  Trench mouth if left untreated, can lead to serious complications and other oral health issues. The infection can spread rapidly and infect cheeks, lips as well as jawbones. Dehydration and tooth loss is another consequence of trench mouth. Infection may also spread and affect other parts of the body, including the organs. Hence, it is extremely important to improve your oral health as well as your overall physical health. Tendency for recurrence once occurred is common leads to progressive destruction of periodontal tissues with typical loss of interdental papilla and formation of characteristic gingival craters. The gingiva retains the concave/ saucer shape (reverse architecture of normal gingiva) as it becomes thickened by fibrous repair tissue.