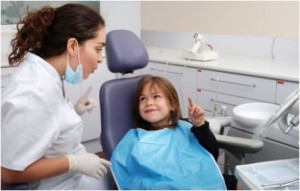
Communicative management is universally used in pediatric dentistry with both the cooperative and uncooperative child. (Chambers, 1976) It comprises the most fundamental form of behavior management in that it is the basis for establishing a relationship with the child which may allow a successful completion of dental procedures and at the same time, may help the child develop positive attitudes towards dental care. It is the means bu which the dentist gets his point across, making himself understood by the use of words or expressions. One should always try to establish communication from the 1st entry into the reception area.
Types of Communications
a) Verbal communication is by speech
b) Non-Verbal (Multisensory communication) is by
-Body Language
-Smiling
 -Eye contact
-Expression of feelings without speaking
-Showing concern
-By touching the child
-Giving him a pat
-Giving a hug
c) Both using verbal and non-verbal
How dentist communicate with you?
- Communication should be comfortable and relaxedÂ
- Language that is chosen should contain words that express pleasantness, friendship and concern. Verbal effects are delineated through selection of words and/or sounds, tone of voice and voice inflection. (Korch 1972)
- Verbal communication is best for younger children more than 3 years of age. Voice that is used should be constant and gentle. Tone of voice can express empathy and firmness. Content of the conversation should be such that from the very beginning the dentist should make you feel that the dentist are your well wishers. The conversation should include by asking your name and age.
- You prefer to be addressed by your name
- Â Sitting and speaking at the eye level allows a friendlier atmosphere.
Use of euphemisms: Euphemisms are substitutes words which can be used in the presence of patient
Choices of words, which is used by the dentist ot staff influence the emotional status of the patient. Therefore , the use of euphemism or reframing is very important while addressing to the patient.
- Anesthetic solution is referred to as water to put the teeth to sleep
- Caries is referred to as a tooth bugÂ
- Rubberdam as a rain coat
- Radiograph as tooth picture
Desensitization
- Joseph Wolfe (1975) used to remove fears and tension in children who have had previous unpleasant dental experience or negative behavior.
Desensitization is accomplished by teaching the child a competing response such as relaxation and then introducing progressively more threatening stimuli.
It is an effective method for reducing a maladaptive behavior.
Methods popularly used nowadays for modifying the behavior by desensitization in children is Tell-Show-Do technique (TSD)
- Addleslon (1959) Â introduced the concept Tell , Show and Do .
- Tell and show every step and instruments and explain what is going to be done
- Continuously and in grades from the least fear promoting object or procedure move to higher grades to more fearful objects.
Indications :
- First Visit
- Subsequent visits when introducing new dental procedure
- Fearful child
- Apprehensive child because of information received from parents/peers
TSD Techinque is applied as follows :
- The dentist using the language that the child can understand, tells the patient what is to be done. It is presented slowly and repeatedly .Â
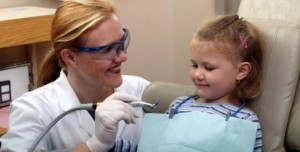
- The dentist demonstrates the procedures to the child using a model or himself and is done slowly.
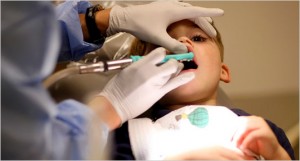
- The dentist proceeds to do the dental procedure exactly as described.
- This is effective in children more than 3 years of age.
Modelling
Introduced by Bandura (1969) , developed from social-learning principle, procedure involves allowing a patient to observe one or more individuals (models) who demonstrate a positive behavior in a particular situation. Therefore the patient will frequently initiate the models when placed in a similar situation. Modelling can be done by :
- Live models – siblings, parents of child n etc…
- Filmed models
- Posters
- Audiovisual aids
Learning through modeling is effective when :
- Observer is in a state of arousal
- When the model has relatively more status and prestige
- When there are positive consequences associated with model’s behavior.
- An important advantage of live modeling is that no additional equipment, personnel or alterations in the dental routine are required.
Contigency Management
It is a method of modifying the behavior of children by presentation or withdrawal of reinforcers. These reinforcers can be :
- Positive reinforcer : is one whose contingent presentation increases the frequency of behavior
- Negative reinforcer : is one whose contigent withdrawal increases the frequency of behavior. Negative reinforcer is usually termination of an aversive stimulus eg : withdrawal of mother
Types of reinforcements can be :
a) Social: eg : praise, positive facial expression, physical contact by shaking hands, holding hands and patting shoulder on the back.
b) Material : may be given in the form of toys , games . Sweets are not given as reward since it causes caries
c) Activity reinforcers : Involving the child in some activity like watching TV shows.