There are a lot of reasons why teeth may get discolored and it is important for the dental practitioner to recognize the underlying cause before deciding on a treatment plan. Discoloration can affect the entire arch (generalized discoloration) or maybe limited to few or several teeth in an arch. (Localized discoloration)Before we discuss on the treatment options for tooth discoloration, here are some reasons that might cause tooth discoloration.Tooth discoloration can be due to extrinsic or intrinsic factors.
Extrinsic factors: (found on tooth surface)
- Due to dietary factors such as coffee, tea, smoking, betel nut chewing, and stains from chromogenic bacteria.
These stains are usually found typically around gingival margin and in less well cleaned areas because these dietary factors tend to stain plaque and pellicle.
- Turner tooth.
Infection of deciduous predecessor can cause enamel hypoplasia in the permanent tooth. (Enamel hypoplasia is a condition where the tooth enamel is hard but thin and deficient in amount)
Intrinsic factors (discoloration of inner tooth structure/dentine)
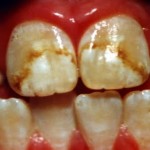
- Dental caries
Arrested dental caries will leave brown stain on your teeth.
2.      Blood pigments
Blood pigments usually affect non vital teeth. (as a result of pulp necrosis)
3.      Tetracycline staining
Administration of tetracycline during tooth formation can cause severe, generalized grey/yellow stains.
4.      Fluorosis
Dental Fluorosis occurs due to excessive usage of fluoride during tooth development.Varies from mild flecks of opaque white enamel to severely hypoplastic patches which take up the extrinsic stains.
5.      Age change. Teeth tend to turn yellower and darker with age.
6.      Tooth development disorders such as amelogenesis imperfecta (teeth are covered with thin, abnormally formed enamel), dentinogenesis imperfecta (abnormal dentine formation) and etc.
 Treatment options for discolored teeth
- Tooth bleaching
There are two types of tooth bleaching techniques: vital and non vital.
Vital bleaching agents ( Carbamide peroxide) They are effective in removing discoloration caused by extrinsic stains. However, if they are used for non vital teeth, it can be difficult to get an accurate shade to match the other vital teeth in the mouth. Vital bleaching agents are placed in a custom tray and repeated until the desired shade is achieved. Carbamide peroxide can cause mild tooth sensitivity and gum tissue irritation.
 Non vital bleaching /internal bleaching are performed after a root canal treatment. The gutta percha are removed from the coronal portion of the pulp chamber. After that, the bleaching agent will be introduced into the pulp chamber and sealed with a temporary filling material.  This procedure can be repeated until a desired shade is obtained.
2. Veneers, direct and indirect composites can also mask tooth discoloration. However they require some amount of tooth destruction (less destructive than dental crowns) and they are more expensive compared to bleaching procedures. Â Vital bleaching agents can be used before placement of veneers to prevent dark enamel and achieve a better translucent effect
3.Dental crowns can be used to mask severe discoloration. They are usually the best alternative if teeth contain extensive restorations.Â
Consult your dental practitioner if you are concerned about your discolored teeth. There are some clinical examinations that should be carried out before deciding on the treatment plan. Â The best way to prevent teeth staining is to brush and floss effectively. If you are a chronic smoker, quit smoking as cigarettes can cause brown staining on teeth which is hard to remove by brushing alone.