ORAL MEDICINE
Oral medicine is defined as that area of special competence concerned with the health of and with diseases involving the oral para oral structures, it includes, principles of medicine that relates to the mouth, as well as research in biological, pathological and clinical spheres, diagnosis and medical management of diseases specific to the orofacial tissues and of oral manifestations of systemic diseases and management of behavioral disorders and the oral and dental treatment of medically compromised patients.
ORAL DIAGNOSIS
Is the act of using scientific knowledge to identify oral disease process and to distinguish one disease process from the other,it is a systematic method of identifying an oral disease process on the basis of facts obtained from the interviews and examination.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Is the process of identifying a condition by differentiating it from all pathological process that may produce similar lesions.
Lichen planus, Leukoplakia & Leukoedema
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
Final Diagnosis is the diagnosis arrived at after all the data has been collected, analyzed and subjected to logical thought
PROGNOSIS
Is the prediction of the course ,duration and termination of a disease and the likelihood of its response to treatment.
CASE HISTORY
It is the planned professional conversation which enables the patient to communicate his or her symptoms, feeling and fear to the clinician. From this information, the clinician obtains insight into the nature of the patients illness and his or her attitude to it
HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS
It is the chronological account of chief complaint and associated symptoms from the time of onset to the time the history is taken.this includes:
Mode of onset of the symptoms
Progress of disease
Treatment which the patient might have received
SYMPTOM
Symptoms are primarily subjective complaints told or expressed by the patient who, may or may not have externally observable elements .
Eg:
Angina pectoris
Neuralgic pain
SIGNS
Signs are those clinical entities which the clinician can observe and record as objective findings.
Eg: pallor, bulla.
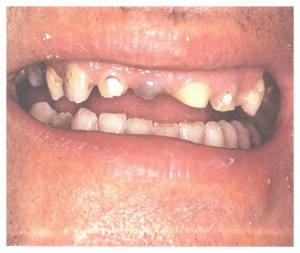
ATTRITION
It is the physiological wearing away of tooth as a result of tooth to tooth contact.
ABRASION
It is the pathological wearing away of tooth substance due to some abnormal mechanical process.
EROSION
Is the loss of tooth substance by a chemical process that does not involve bacteria
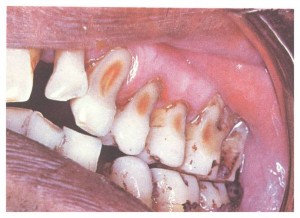
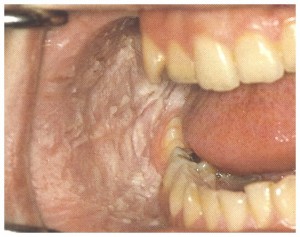
WHITE LESIONS
Is a non specific term given to an abnormal area of oral mucosa which appears whiter and of a different texture than the adjacent normal mucosa.
KERATOTIC WHITE LESION
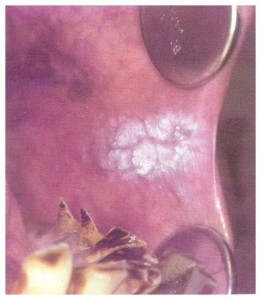
White lesions which resist scraping or rubbing
Eg:leukoplakia
NON KERATOTIC WHITE LESION
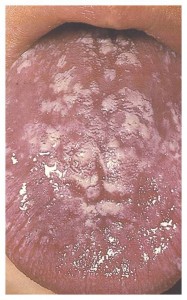
White lesions that are easily dislodged with gentle rubbing or scraping
Eg:Pseudomembranous candidiasis,
RED LESION
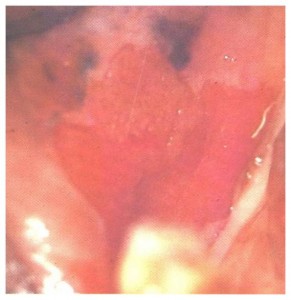
Is an area of reddened mucosa that is either smooth or has a granular or velvety texture
Eg: Erythroplakia
TUMOUR OR NEOPLASM
Mass of tissue formed as a result of abnormal, excessive, uncoordinated, autonomous and purposeless proliferation of cells and persist in the same excessive manner even after cessation of the stimulus that evoked the change.
OR
It is a progressive ,purposeless, perverted, persistent proliferation of tissue
Eg: squamous cell carcinoma

CYST
It is defined as a pathological cavity containing fluid, semi fluid or gaseous material and is usually lined with epithelium.
HAMARTOMA
Tumor like malformation characterized by presence of particular histologic tissue in improper proportions as distribution with a prominent excess of one type of tissue .
Eg:haemangioma.
HAEMANGIOMA
Tumor like malformation, composed of seemingly disorganized masses of endothelial lined vessels that are filled with blood and connected to the main blood vascular system.
NEVUS
Circumscribed new growth of skin or oral mucosa of congenital origin presenting as small ,elevated flat pigmented lesion.
Eg: white sponge nevus,blue nevus.
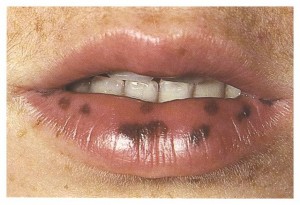
MACULE
Well circumscribed , flat lesions that are noticeable because of their change from normal skin colour.
Eg:vitiligo, petechaie, melanin deposits in Addison disease.
PAPULE
solid lesions raised above the skin surface that are smaller than 1cm in diameter, papules may be seen in a wide variety of diseases.
Eg: warts, nevi {moles} Fordyce’s granules
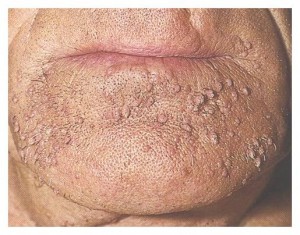
NODULE
These lesions are present deep in the dermis and the epidermis and can be easily moved over them. These are solid lumps generally 1cm or more in diameter . They may be seen as an elevation or can be palpated within the skin.
Eg: fibroma, neurofibroma
VESICLES
Blister containing clear fluid that are less than 1cm in diameter.
Eg:herpes simplex, chickenpox, acute tenia pedis
BULLAE
Elevated blister like lesions containing clear fluid that are over 1cm in diameter.
Eg: herpes zoster, pemphigus, second degree burns, insect bite.