 Chronic periodontal disease is a disease which involves the destruction of gums and supporting tissues. This disease is often seen in adults and is the commonest cause of adult tooth loss. Before we proceed to discuss about the symptoms of chronic periodontal diseases, let us have a look at the characteristics of healthy gums.
Chronic periodontal disease is a disease which involves the destruction of gums and supporting tissues. This disease is often seen in adults and is the commonest cause of adult tooth loss. Before we proceed to discuss about the symptoms of chronic periodontal diseases, let us have a look at the characteristics of healthy gums.
Here are some characteristics of healthy gums:
- Â Healthy gums are pale pink/coral pink in color. Slight brown pigmentation is normal especially in African, Asian or Mediterranean patients. Â Gum depigmentation or gum bleaching is a cosmetic dentistry procedure used to remove black spots on gums caused by excessive melanin deposition.
- Â Â They are knife edged, scalloped to conform to the contour of the teeth.
- Â Â Â Healthy gums are firm and resilient upon palpation.
-    No periodontal pockets are found in healthy gums. Periodontal pockets are formed when gum    pull away from teeth and a space is formed. The depths of periodontal pockets can be measured by using a periodontal probe.
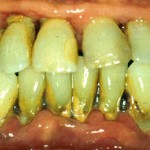
Chronic gingivitis
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of periodontal disease and one of the most obvious effects of gingivitis is bleeding gums. However, most people will believe that bleeding gums are normal and will not take it seriously. When gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress into periodontitis.
Clinical features of chronic gingivitis:
- 1.      Your gums will be red in color, swollen and can bleed easily when you brush your teeth.
- 2.      The surface of your gums can be smooth and glossy.
- 3.      You will feel sore while brushing your teeth.
- 4.      You might notice the taste of blood.
If you are facing any signs and symptoms mentioned above, you may have gingivitis and actions should be taken to reverse this condition. The most common treatment of gingivitis is to brush well and attend regular scaling appointments to minimize plaque irritation.
Here are some symptoms of chronic periodontitis
1.      History of bleeding gums before and after tooth brushin
2.      Formation of gingival pockets.  Pocketing of 4mm is likely to indicate an early chronic periodontitis.
3.      Gingival recession (gums may pull away from teeth, making them look longer) may accompany chronic periodontitis but is not a necessary feature of this disease. Gingival recession can occur if you are not having chronic periodontitis.
 4.      Loose teeth and new spaces can develop around your teeth as a result of chronic periodontal disease.
5.      Discomfort
Gingival recession and root exposure may cause you sensitivity when taking hot and cold drinks.
6.      Alveolar bone loss
Destruction of surrounding tissue including the alveolar bone is the important feature of chronic periodontitis and this will eventually lead to adult tooth loss.(Alveolar bone is the specialized bony structure that supports your teeth.
7.      Halitosis/bad breath
Patients with chronic peridontitis may have halitosis and offensive taste which results from production of pus which exudes from pockets.
Please consult your dental practitioner if you are facing any of these symptoms. You should seek early treatment to prevent the disease from developing further.
Â