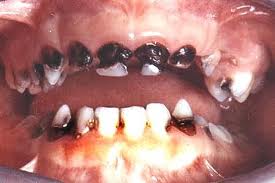
1. Why extract a baby tooth?
Choosing between extraction and filling or conservation is a very common decision that both dentists and patients have to take every day. With adults the decision making is much easier, if the tooth is restorable and the patient can pay for the treatment then we simply conserve the tooth. If the patient is a child then the process of decision making is much harder as many factors affect the selection of the treatment plan that the dentist have to follow.
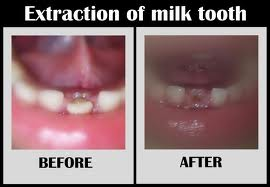 Extraction of a baby tooth may prove necessary as part of orthodontic treatment, or because of injury or decay.
Extraction of a baby tooth may prove necessary as part of orthodontic treatment, or because of injury or decay.
- Child’s age:
- This factor is very important as it well judge the cooperation of the child during treatment process so the cooperative patient is giving more chance to the success of lengthy treatments like filling or even root canal when uncooperative patient may drive the dentist to extraction.
- The time left for the tooth to come out or shedding:
- The dentist here estimate the time left for the milk tooth in the mouth by considering the normal eruption time averages and also the eruption time variations of your kid. Some kids tend to change their teeth earlier of later than normal and this should be taken in consideration when the dentist calculates the estimated of the milk tooth left.
- If the dentist estimated that the permanent tooth needs only 6 months or less to come out then it would be better not to waste money and time in filling or root canal.
- We have to know that premature extraction of the milk teeth will result in less effective chewing also may cause malalignment or crowding in the permanent teeth which will need an expensive orthodontic treatment after that.
2. How can extractions aid orthodontic treatment?
- If crowding is likely to occur while baby teeth are being replaced by permanent teeth, then some baby teeth may have to be extracted.
- These planned extractions should create enough space for the permanent teeth to erupt into and for them to be properly aligned.
- The extractions may avoid the later need for complicated orthodontic treatment.
3. Will injured baby teeth have to be extracted?
- If a baby tooth has been forced into the jaw by a blow or a fall, and has damaged the underlying permanent tooth, the baby tooth will need to be extracted.
- If an injury causes the death of the nerves and blood vessels of a tooth, it may be necessary to extract the tooth.
- A pulpotomy may be possible, but if the pulp becomes infected and causes an abscess to develop, extraction is called for.
- The developing permanent tooth below it may erupt malformed or discoloured.
- The fate of the permanent tooth is always given priority in such cases.
4. What are the signs of injury to baby teeth?
- Bleeding and pain are the main signs of injury.
- Bleeding is a common sign of injury.
- The crown of the tooth may be chipped, cracked or completely severed.
- Pain will vary according to the extent of the damage to the tooth.
It may be severe if an abscess develops.
Biting or chewing can also be painful. - A tooth loosened by injury and unable to be stabilised may have to be extracted.
Observation over a few weeks will indicate if the tooth will survive.
Splinting of the tooth by the dentist will assist stabilisation. - Brown to black discolouration may follow the death of the nerves and blood vessels of a tooth.
This is the result of the breakdown of blood cells and follows the same pattern as that of a bruise to the skin.
5. Why do decayed baby teeth sometimes need to be extracted?
-
Extraction is necessary when the decay is so widespread that it cannot be repaired with either a filling or a cap (crown).
- Extraction of a baby tooth may be unavoidable when the decay has led to infection and the formation of an abscess at the end of the root.
This infection could be very painful and could affect the growth of the permanent tooth below.
6. Can the extraction of baby teeth lead to problems?
- The extraction of baby teeth, especially back teeth, allows adjacent teeth to drift into the empty space.
- The narrowing of this space may affect the normal eruption of the permanent teeth which will replace them.
- The movement of the adjacent teeth into the space can result in crowding of the permanent teeth, with the subsequent need to have them straightened.
- However a space-maintainer can be fitted by the dentist to prevent the drifting of teeth.
- Always consult your dentist if a baby or child’s tooth is injured.