There has been an increase in adults seeking orthodontic treatment over the recent years and it can be due to various reasons that include:
- Improved dental awareness with the advent of preventive dentistry and teeth are retained longer in the mouth.
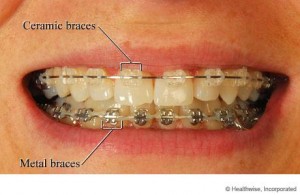
- The issue of esthetic concern has reduced due to the introduction of ceramic and lingual brackets.
- Orthodontics or the wearing of teeth braces is now socially acceptable and can be a sign of affluence.
- Recommended by general dentists for restorative and periodontal care.
- Insurance and claims for dental treatment in some countries.
Problems in orthodontic treatment for adults
Orthodontic treatment is usually carried out in children during their puberty stage and/or as soon as their permanent teeth have erupted as more tooth movement can be accomplished at that stage. Braces for teeth can be placed later in adulthood but treatment may be complicated by some factors including:
- Lack of growth – major skeletal problems would need to be corrected by orthognathic jaw surgery.
- Decreased blood supply to tissues in the mouth and loss of gum attachment – light force can only be used and movement of teeth will be slower compared to orthodontic treatment in a child.
- Missing and heavily restored teeth – missing teeth can lead to physiological movement of teeth and/or tilting of teeth and to over-eruption of opposing teeth, which can cause maligned bite.
Orthodontic treatment – adult versus children
Criteria |
Adults |
Children |
| Growth | Negligible | Significant growth spurt and tenable for growth modification
|
| Blood supply to tissues and cell turn over | Reduced – longer time for tissue reorganization | Increased – rapid cellular response
|
| Periodontal status | Reduced attachment, necking of jaw bone, periodontal disease, only light forces can be used
|
Increased width of periodontal ligament, can tolerate heavy forces |
| Dental status | Missing/heavily restored teeth, supra eruption | Physiological tooth movement during eruption
|
| Occlusal discrepancies | Reduced tolerance to occlusal discrepancies, can lead to temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disease
|
Greater adaptation to occlusal changes with growth |
| Appearance of appliance | Great concern, preference for discretion | Less concern (may choose to show off)
|
| Speech tolerance | Difficult to adjust | Adjust quickly
|
| General health | Careful consideration needed prior to treatment | Usually little concern
|
| Co-operation and compliance | Positive and well motivated (internal) | Varies greatly, usually parental pressure (external motivation)
|
| Treatment appreciation | Very appreciative and interactive with feedbacks
|
Usually not concerned |
Treatment planning principles for adult teeth braces
- Considerations made to current medical problems for the taking of steroids or bisphosphonates can affect the bone cell turnover and in turn affect tooth movement.
- Priority is usually made for restorative and periodontal treatment.
- The periodontal status is assessed using full mouth intraoral periapical radiographs (IOPAs) for jaw bone height as well as constant evaluation and periodontal therapy during treatment.
- Biomechanical consideration is made as there is loss of jaw bone height and apical shift of centre of resistance due to accumulation of plaque, tartar, or bone loss that can make tooth movement difficult.
- The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) condition and path of closure is assessed such as missing teeth, and occlusal discrepancies as establishing functional bite is important.
- Skeletal problems and severe malocclusion like deep bite can only be treated by surgical option.
- Anchorage planning varies based on teeth present.
- Age changes in bone with more of cortical and less cancellous bone, which decreases tooth movement.
- Only light force due to reduced periodontal ligament or supporting tooth tissues width with longer intervals between appointments as no physiological movement present.
- Headgears rarely used but useful for anchorage if patient co-operates.
- Tooth colored appliance and lingual orthodontics are usually requested in adults.
- Longer treatment time and usually permanent retention would be required for the modified bite to stay in place.
Adjunctive orthodontics
Adjunctive orthodontics is an integrated treatment planning for comprehensive treatment involving orthodontics and other dental specialties. Adults with mutilated dentition requiring restorative, periodontal, and prosthetic treatment may require orthodontics or dental braces for:
- Redistribution or closing spaces in between teeth
- Uprighting of tilted abutments (prostheses supporting teeth)
- Intrusion of supra-erupted teeth
- Extrusion of fractured teeth
Principles of adjunctive orthodontics
Adjunctive orthodontics are usually done to facilitate adequate restoration of decayed teeth, improve periodontal health by eliminating plaque harboring areas and/or to establish favorable crown root ratio for axial loading of teeth in the making of prostheses.
Periodontally compromised dentition or mouths with weak tooth supporting tissues usually results in pathological tooth migration or shifting of tooth. This is due to:
- Reduced bone support that allows teeth to succumb to adverse soft tissue and biting forces
- Periodontal inflammation causes extrusion of teeth resulting in traumatic bite and eventually teeth drift
- Premature contacts can cause drift of periodontally compromised teeth for example proclination (forward inclination) of upper front teeth due to forward shift of lower jaw
- Lack of posterior support can cause excessive loading of front teeth that leads to proclination
How much would adult braces cost?
The cost of braces for adults can be a significant financial investment though most find it worthwhile. Typical orthodontic treatment costs between $3,000 and $7,000 in the US. An accurate estimate would be difficult to provide since treatment costs vary depending on each individual and the problems they face. For example, an individual who needs very minor teeth adjustments may require only a retainer which costs around $500 to $1,000 compared to an individual with severe teeth problems that may escalate cost to $7,000.
Due to variation in regional overhead, there can be significant differences in fee charges. Same goes for the type of braces you opt for – traditional metal braces can start from $5,000 onwards, ceramic brackets will need an additional $500 while an extra $2,000 to $5,000 is required for lingual braces. The national average price for Invisalign braces is about $5,000 with a starting price of $3,500.