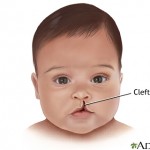
Cleft lip and cleft palate are birth defects affecting the mid facial region. Patients with cleft lip might have a small notch on the lip or a wide opening which involves the lip and the palate ( the roof of your mouth) The exact cause of cleft lip/palate is unknown but it is believed that genetic, usage of certain drugs during pregnancy, viruses, toxins are the causative factors of cleft lip and palate.
Detection of cleft lip/palate
Detection of cleft lip/palate can be detected during pregnancy by an ultrasound screen or a three dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. Detection during the pregnancy stage will prepare the parents mentally and allow them to understand the condition.
Prevalence of cleft lip and palate
Approximately 1 in 1000 children born has cleft lip/cleft palate. The incidence of cleft lip and palate varies by race. The native Americans have the highest incidence of cleft lip/cleft palate whereby the African Americans have the lowest incidence.
Types of cleft lip and palate
1)     Cleft lip: cleft which occurs on the lips (without affecting the palate) It may varies from a small notch(this is known as incomplete cleft), to a complete cleft (which extends from the vermillion border of the lips to the floor of the nose)
2)Â Â Â Â Â Cleft palate: cleft which occurs on the palate without affecting the lips
3)Â Â Â Â Â Cleft palate and lip : affects both lips and palate.
Cleft which occurs on only one side of the lip is known as unilateral cleft whereby cleft which involves both sides of the lips is known as bilateral cleft.
Problems in cleft lip and cleft palate patients
1)Â Â Problem in feeding
Feeding can be a problem in cleft babies.  A cleft baby is unable to generate a positive pressure which is needed to suck the milk from the breast or milk bottle. As a result of cleft, there can be a communication between the oral and nasal cavity which causes nasal regurgitation during the feeding process.
What we can do to overcome this problem:
-         Mother can breast feed the cleft baby in an upright position. This will minimize the consequence of nasal regurgitation(milk coming out from the infant’s nose)
-         Specially designed bottles such as Haberman bottle can be used to overcome the baby’s lack of suction. They are designed to allow the feeder to be activated by tongue and gum pressure rather than by sucking.
-Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â The nipple can be positioned to the non cleft side (for infants with unilateral cleft)
-Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Feeding plate can be constructed as soon after birth to allow assist feeding. It is a small plastic plate which covers the cleft area. It will also help to prevent the collapse of palate in infants with bilateral cleft palate. Â
2)Â Â Â Â Â Aesthetics problem
Aesthetics can be a problem in patients with unrepaired clefts. Â Surgery is often indicated at an early age to avoid and minimize future esthetic problems. Â
3)Â Â Â Â Â Speech development
Speech problems can occur especially in cleft palate patients due to velopharyngeal dysfunction. Velopharyngeal dysfunction refers to a condition where by there is improper closing of the soft palate of the mouth during speech. This will allow air to escape through the nose instead of the mouth, producing a nasal tone in the voice. Patients with velopharyngeal dysfunction will not be able to pronounce consonants sounds such as “p†,â€dâ€,â€tâ€,â€dâ€.  Thus, speech therapy is sometimes required in cleft patients.
4)Â Â Â Â Â Middle ear infection /Otitis media
Patients with cleft lip/palate are more prone to fluid buildup in the middle ear. Repeat ear infections can also causes hearing loss in cleft patients. Hence it is important to monitor the hearing and middle ear function of cleft infants.
5)Â Â Â Â Â Dental problems and malocclusion
Children with orofacial clefting have more dental problems than other children.
Dental problems such as missing teeth, extra tooth, abnormal size/shape of tooth can be presented in cleft patients. There is also an increased need for orthodontic intervention to correct the present/developing malocclusion.
A typical cleft palate team consists of :
Â
-Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Plastic surgeons (to perform lip and palate repair surgery)
-Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Pediatric dentists (to perform annual dental review on patient and make initial contact with the parents)
-Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Orthodontists (to perform orthodontic treatment)
-Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Speech pathologist (to correct developing speech)
-Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Medical officers (cleft lip/palate is also associated with 300 medical syndromes)
-         ENT surgeons (monitor patient’s hearing ability)
-Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Social workers (to provide counseling to both parents and child)
-Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â
Â
Â
Â
Â