BUCCAL BIFURCATION CYST
SYNONYMS
Mandibular infected buccal cyst,
Paradental Cyst,
Inflammatory collateral dental cyst
Inflammatory lateral periodontal cyst
Craig’s cyst
Author Archives: meifong
Radiographic Appearance of Cysts Part 1
Definition
A cyst is a pathological cavity in hard and soft tissues having fluid or semi-fluid or gaseous contents, that are not created by the accumulation of pus frequently, but not always lined by epithelium.
Continue reading
Radiographic Faults and Artifacts Part 2
Radiographic Faults and Artifacts Part 1
THE IDEAL RADIOGRAPH IS THE ONE WHICH SHOWS:
1. Optimum density
2. Optimum contrast
3. Accurate
4. Covers the area of interest completely
When any of the above conditions are not satisfied it may be termed as the faulty radiographs.
Working Length Determination in Root Canal Treatment Part 2
Tear drop silicone – rubber stops have an added advantage because they do not have to be removed form the instrument during sterilization at 4500 F and tear drop tip can be positioned to indicate instrumental curvature
Rubber stops instruments have certain disadvantages like movement of up (or) down the shaft, leading to short (or) past the apical constriction and time consuming.
Working Length Determination in Root Canal Treatment Part 1
WORKING LENGTH DETERMINATION
In detail endodontic procedure primarily consists of
-        Access preparation –LA in vital
-Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Pulpectomy
-Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Working length X-ray
-Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Biomechanical preparation (cleaning and shaping)
Chemo-mechanical preparation disinfection
Obturation
Clinical Diagnostic Methods Part 3
Recent advances in diagnostic methods
1. RADIOVISIOGRAPHY
2. XERO – RADIOGRAPHY-
3. PULSE-OXIMETRY:
4. LASER DOPPLER FLOWMETRY
5. COMPUTERISED TOMOGRAPHY
6. DIGITAL SUBTRACTION RADIOGRAPHY
7. MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
8. COMPUTERISED EXPERT SYSTEM.
9. THERMOGRAPHIC IMAGING.
10. TACT:( TUNED APERTURE COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY)
Clinical Diagnostic Methods Part 2
Radiograph
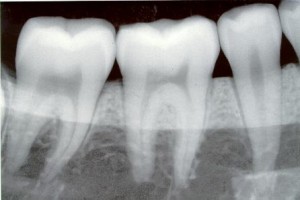
Radiograph may show the number,
Course,
Shape,
Length,
and width of root canals, the presence of calcified material in the pulp chamber or root canal,
The resorption of dentin originating within the root canal (internal resorption) or from the root surface (external resorption)
Calcification or obliteration of the cavity,
Thickening of the periodontal ligament resorption of cementum,
And nature and extent of periapical and alveolar bone destruction.
Clinical Diagnostic Methods Part 1
Correct treatment begins with a correct diagnosis. Arriving at a correct diagnosis requires
1) Knowledge
2) Â Skill
3) Art
What is Obturation in Root Canal Therapy Part 3
Compaction Method:
Introduced by Mc spadden
– This method uses heat to decrease G.P viscosity and increase its plasticity
– The heat is created by rotating a compacting instrument in a slow-speed hp at 8,000-10,000 r.p.m alongside G.P cones inside the canal.