Types of herpes simplex virus
There are 8 types of herpes simplex virus which affect human beings. Â
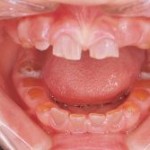
Type I herpes simplex virus / oral herpes : Â causes primary herpetic gingivostomatitis and cold sores around your mouth.
Type 2 herpes simplex virus/ genital herpes : can cause severe oropharyngeal infection and it is usually transmitted through sexual contact.
Type 3 herpes varicella zoster virus: causes chicken pox among children Continue reading