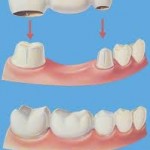
 Having a missing tooth and worried about presence of a gap between your teeth which disrupts your daily social life and compromises your appearance. Worry less as dental bridges offer a great solution by closing the gaps. A false tooth is held in the open space at the gum line by attaching it to teeth on either side of the missing tooth. If several teeth are missing, artificial teeth are glued together and attached to adjacent real teeth. Dental implants and removable partial denture are other options available to replace missing tooth. Likewise other dental procedures, dental bridges have its advantages and disadvantages as well. Continue reading
Having a missing tooth and worried about presence of a gap between your teeth which disrupts your daily social life and compromises your appearance. Worry less as dental bridges offer a great solution by closing the gaps. A false tooth is held in the open space at the gum line by attaching it to teeth on either side of the missing tooth. If several teeth are missing, artificial teeth are glued together and attached to adjacent real teeth. Dental implants and removable partial denture are other options available to replace missing tooth. Likewise other dental procedures, dental bridges have its advantages and disadvantages as well. Continue reading
Category Archives: Dental Care Gum
Diabetes and Gum Disease
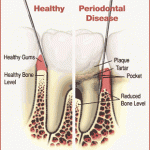
What is gum disease?
Gum disease is an infection in the gum tissues and bone that keep your teeth in place. There are two types of gum disease, gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Gingivitis is the inflammation of gums caused by bacteria and plaque. This form of gum disease does not include any loss of bone and tissue that hold teeth in place. It is reversible. If left untreated, it can progress to a more severe form, periodontitis, which is irreversible.
- Periodontitis is the inflammation around the tooth. Gums pull away from teeth and form spaces, which become infected as bacteria and plaque spreads. Eventually, the bones, gums and tissue that support the teeth are destroyed. As a result, teeth become loose. Continue reading
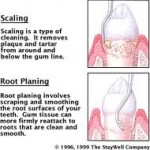
What is Deep Gum and Root Cleaning?
Deep gum cleaning consists of scaling and root planing. Gum disease (gingivitis) if untreated can progress to more
serious periodontal disease (bacterial/viral proliferation which overwhelms the host immune response) causing destruction of the supporting tissues of the teeth and bone loss which are irreversible in nature. A periodontal pocket forms and harbors bacteria in large amounts. Deep scaling and root planning are the therapeutic procedures performed to heal your gums by removing the disease causing toxins. Scaling is the process of removing dental tartar from the teeth surfaces while root planning involves removing infected tooth structure (dentin and cementum) and smoothing the rough root surfaces of the teeth. The goal of active therapy is to remove as much subgingival debris as possible and disrupt/ the bacterial proliferation. Continue reading
How to Identify Symptoms of Trench Mouth
What is Trench Mouth?
Trench mouth is also known as Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (ANUG) or Vincent’s infection. It is an acute
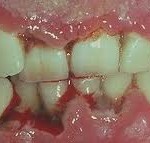
ANUG
 necrotizing inflammatory disease produced by endogenous infection where systemic changes, predispose the gingiva to invasion by bacteria. A recurring periodontal disease which results in necrosis and ulceration of the gums. It is a communicable infection of the respiratory tract and mouth extending to the tongue, palate, throat and pharynx. ANUG is a mixed bacterial infection with predominant groups of anaerobic bacteria, the fusiform, spirochetes and treponema. They present in large numbers in slough and necrotic tissue at surface of the ulcer and invade a small distance into underlying connective tissue, releasing toxins and enzymes. Trench mouth is a serious oral disease which causes severe pain and major discomfort. Inability to carry out good oral hygiene and poor nutritional status are the contributing factors of trench mouth. Other causes include smoking, increased physical and emotional stress, age, poverty and infections like HIV, AIDS and measles, malignant tumors and acute leukemia.
Homeopathic Remedies for Gingivitis
What is gingivitis?
Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gum tissue. It  most commonly occurs in response to bacterial biofilms on the tooth surface, also called plaque. Therefore this form of gingivitis is termed ‘plaque induced gingivitis’. Gingivitis can also occur due to other causes such as hormonal change (eg.pregnancy), systemic diseases (eg. diabetes) and blood dyscrasias. If gingivitis is not treated at the early stage, it may progress to periodontitis, a destructive form of periodontal disease which is characterised by bone loss, pocketing and gum recession. Continue reading
How to Take the Best Care of Your Child’s Teeth
A child’s teeth start to develop before birth. Therefore, it is necessary to start caring for your child’s teeth and gums at an early age. The most important is to bring your child to the dentist when his first tooth erupts into the oral cavity, usually around 6 months of age. The dentist will be able to detect any problems associated with your child’s teeth before they become serious. Establishing a good rapport between the dentist and child is essential to ensure that the child feels safe and able to cooperate during dental treatment. Diet, proper tooth brushing and oral hygiene goes hand-in-hand with your child’s care. Continue reading
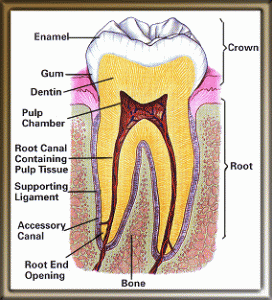
How to stop bone loss in teeth naturally
What does it mean by dental bone loss?

Bone loss
For our convenience, the term bone loss is differentiated to two types in our mouth. The loss of bone specifically involving jaw (alveolar) bone area but are not involving teeth is referred as dental bone loss. Meanwhile, teeth bone loss means loss of roots of teeth or the jaw bone surrounding teeth. At times, it is possible to have both bone loss happening simultaneously. Continue reading
How does Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS) lead to canker sores?
What are Canker sores?
Canker sores are also known as aphthous ulcer. Patients will normally face symptoms such as soreness, burning, or prickling sensation 1 to 2 days before the appearance of the ulcers.
Normal surrounding of your mouth will appear normal or there will be some red macules at the future sites of the ulcers. There are three recognisable type of aphthous ulcers , minor aphthous ulcers, major aphthous ulcers, and herpetiform ulcers. Continue reading
Broken Teeth
Broken Teeth and Fractured Teeth Overview
Our teeth are very strong. We have an outer layer of enamel covering which can only be sectioned or cut with diamond coated drills. However, over the years due to hard diets or decay of tooth, the tooth structure of enamel becomes weakened. That is when our tooth can chip and have a fractured tooth (cracked tooth) and also a broken tooth.
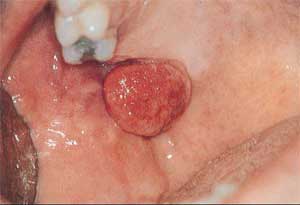
Causes of Gum Swellings and Lumps Part2
Continued from Part1.
8)Â Â Â Â Â Giant cell tumor
A giant cell tumor is one that is made up of a large number of benign (non-cancerous) cells that form an aggressive tumor. Also called peripheral giant cell granuloma, it usually forms as a response to trauma or some chronic inflammatory process.
Management: Surgical removal of tumor and removal of possible causative factors to avoid reoccurrence. Continue reading