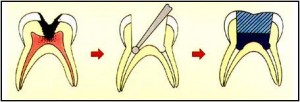
Post design
Posts (or dowels) can generally be divided into two main subgroups, depending on how retention is achieved. Active posts derive their primary retention directly from the root dentine by the use of threads. Passive posts on the other hand gain retention as their name suggests by passively seating in close proximity to the post hole walls, and rely primarily on the luting cement for their retention. Each post type can further be subdivided according to its general shape, that is whether it is tapered or parallel sided. In general, active posts are more retentive than passive posts of a similar configuration, and parallel-sided posts are more retentive than tapered posts. Post choice should therefore be dictated by each clinical situation. Continue reading