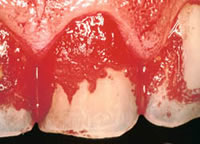
With these concepts in mind, let us review the histology of the periodontal pocket, especially in the area of tissue destruction and healing after the periodontal therapy instituted. The periodontal pocket is described as one which occurred with destruction of the supporting periodontal tissues. Progressive pocket deepening leads to destruction of the supporting periodontal tissues and loosening and exfoliation of the teeth. The suprabony pockets are those which the bottom of the pocket is coronal to the underlying alveolar bone. The infrabony pockets are those which the bottom of the pocket is apical to the level of the adjacent alveolar bone and the lateral pocket wall lies between the tooth surface and the alveolar bone. Continue reading
Category Archives: Gingivitis
New attachment and reattachment Part 1
The goal of Periodontal therapy is to halt the disease progression and prevent its recurrence, and restore the lost periodontal structure which occured as the result of the disease destruction. The later goal prompts us to evaluate the concept of “new attachment†or “regenerationâ€, and “reattachment†or “repairâ€. Each concepts will lead to different mode of periodontal therapy, and ultimately different result. New attachment is the ideal, desired goal, which each periodontist today are trying to achieve in every possible way. Continue reading
Types of Scalers
The American Academy of Periodontology published a position in paper summarizing what is known about these instruments and how they compare in their effectiveness (J. Periodontol 2000:71;1792-1801). Recent modifications of tip design for power driven scalers provide improved access into deep pockets and difficult to reach areas such as furcations. Therefore, studies were undertaken to shed light on the potential roles of sonic and ultrasonic scalers in periodontal therapy. Continue reading
Is Dental Plaque the Main Cause of Dental Caries?
Our mouth is constantly bathed in saliva and is exposed to the passage of food, the oral flora and many other stimuli considering the variety of objects that people put in their mouths such as cigarettes, pipes, hair-grips and so on. Nevertheless, our mouth has a remarkable ability to resist and adapt according to these stimulations. Our teeth are also exposed to the same factors and they can be covered wholly or in part by food debris, soft and hard deposits.
Â
Dental Plaque, the main cause of Dental Caries
Dental Plaque is a soft but adherent deposit of bacteria and their products, which forms on all tooth surfaces and other objects in the mouth, for example; fillings or dentures. This Plaque formation is a natural, physiological process and is an example of a biofilm, which means it is not a haphazard collection of bacteria but a complex association of many different bacterial species living together in a single environment. For instance, a newborn baby’s mouth is sterile but within a few hours, microorganisms appear; mainly Streptococcus salivarius. By the time the baby had his/ her first tooth out, a complex flora is established.
Â
Basically, Dental Plaque is scarcely visible in thin layers and it can be revealed only by the use of a Plaque-Disclosing Agent. In thick layers, it can be seen as yellowish or grey deposits which cannot be removed with mouthwashes or by irrigation but can be brushed off. It is usual to find it on areas which are difficult to reach by tooth brushing, for example; in between teeth or in severely crowded teeth. When Dental Plaque calcified or mineralized, it will become Dental Calculus or commonly known as Tartar. It is a ‘stony crust’ that forms on teeth and has long been associated with Gums Disease. Having said that; Dental Plaque is the main cause of dental caries.
Â
Â
     Â
Â
Â
Â
      Â
    Â
Â
Â
Â
Continue reading
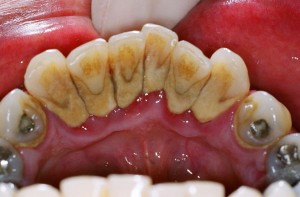
Causes of gum bleeding
Causes of gum bleeding
1.     Gum diseases
A. Gingivitis.
Gingivitis comes from the word “gingiva†which means gums and “-itis†which means inflammation, hence gingivitis means inflammation of the gums. Poor tooth brushing technique or the lack of it leads to accumulation of plaque around the teeth, and eventually leads to gum diseases such as gingivitis. You should suspect gingivitis when you have other symptoms such as :
i)Â Â Â Â Â Â altered appearance of your gums (deep red in colour, soft and swollen appearance, loss of a scalloped and knife-edge shape)
ii)Â Â Â Â discomfort and pain
iii)Â Â Â unpleasant taste
iv) Â Â bad breath or halitosis Continue reading
How to Regrow Gums
Everybody loves to smile, but lately you’ve been hating it because of the state of your teeth and gums. They are a mess, especially your receding gumline. You’re absolutely certain your smile looks more like a jack-o-lantern’s grimace than a genuine expression of warmth. You don’t need to clamp your mouth shut forever, but rather take a stab at a few methods that may help you regrow gums. Gum disease is the leading cause of extensive of gum damage. Feel fortunate that you found out the problem before you developed things like loose and sensitive teeth. If you already have sensitive or loose teeth, don’t waste any more time. Get yourself back to your dentist to get help with your receding gum problem. It’s always helpful to walk in with some knowledge of the receding gum treatments. Continue reading
How Neem Works
In the old days the people in India did not use neem toothpaste. They used neem toothbrushes instead. Chewing on a neem twig has for many centuries been the commonly preferred way to prevent gum disease and maintain healthy teeth. These rural people had never used a “real” toothbrush, didn’t know Crest or Colgate, yet they had perfect teeth. A perfect natural solution. Researchers believe the tradition of using neem twigs for dental care has helped Indian villagers to avoid cavities and tooth loss, although they have no access to modern dental care facilities or products. Continue reading
Questions and Answers : Gums
What are gums?
Gums are also known as gingival. They are part of oral tissues which support our teeth and cover the bone. Â  Continue reading
Continue reading
How to Prevent Gum Recession With a Tongue Piercing
If you have or want to get your tongue pierced, it is important to receive proper care to avoid infection and gum recession. Gum recession, or periodontitis, is a very common problem with tongue piercings due to the jewelry rubbing against the gums. This can eventually lead to exposed roots, which cause much pain and, eventually, loss of teeth.
When considering lip piercing, you should be aware of the risks that you may encounter while wearing lip ring. To avoid the most common risks of a lip ring piercing, book an appointment with a professional piercer to discuss your desire to get one. Ask about the healing process, and how you can avoid damage to your teeth and gums while wearing a lip ring. Continue reading
Laser Dental Cleaning
Lasers have been used in dentistry since 1994 to treat a number of dental problems. But, despite FDA approval, no laser system has received the American Dental Association’s (ADA) Seal of Acceptance. That seal assures dentists that the product or device meets ADA standards of safety and efficacy, among other things. The ADA, however, states that it is cautiously optimistic about the role of laser technology in the field of dentistry. These lasers are different from the cold lasers used in phototherapy for the relief of headaches, pain, and inflammation. Continue reading