The peripheral giant cell granuloma has an unknown etiology, with some dispute as to whether this lesion represents a reactive or neoplastic process. However, most authorities believe peripheral giant cell granuloma is a reactive lesion. Continue reading
Category Archives: Gum Disease
Types of papillae on tongue
Taste buds contain the receptors for taste. They are located around the small structures on the upper surface of the tongue, soft palate, upper esophagus and epiglottis, which are called papillae. These structures are involved in detecting the five (known) elements of taste perception: salty, sour, bitter, sweet, and umami. Via small openings in the tongue epithelium, called taste pores, parts of the food dissolved in saliva come into contact with taste receptors. These are located on top of the taste receptor cells that constitute the taste buds. The taste receptor cells send information detected by clusters of various receptors and ion channels to the gustatory areas of the brain via the seventh, ninth and tenth cranial nerves. Continue reading
Desquamative gingivitis
Desquamative gingivitis is a cutaneous condition characterized by diffuse gingival erythema with varying degrees of mucosal sloughing and erosion.
A band of red atrophic or eroded mucosa affecting the attached gingiva is known as dequamative gingivitis. Unlike plaque-induced inflammation it is a dusky red colour and extends beyond the marginal gingiva, often to the full width of the attached gingiva and sometimes onto the alveolar mucosa. DG is more common in middle-aged to elderly females, is painful, affects the buccal/labial gingiva predominantly. Some reserve the term for cases where the epithelium blisters or peels while others use it whenever the characteristic red appearance is present. (Edward W. Odell, 2010) Continue reading
Causes of gum bleeding
Causes of gum bleeding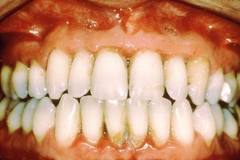
1.     Gum diseases
A. Gingivitis.
Gingivitis comes from the word “gingiva†which means gums and “-itis†which means inflammation, hence gingivitis means inflammation of the gums. Poor tooth brushing technique or the lack of it leads to accumulation of plaque around the teeth, and eventually leads to gum diseases such as gingivitis. You should suspect gingivitis when you have other symptoms such as :
i)Â Â Â Â Â Â altered appearance of your gums (deep red in colour, soft and swollen appearance, loss of a scalloped and knife-edge shape)
ii)Â Â Â Â discomfort and pain
iii)Â Â Â unpleasant taste
iv) Â Â bad breath or halitosis Continue reading
How to Regrow Gums
Everybody loves to smile, but lately you’ve been hating it because of the state of your teeth and gums. They are a mess, especially your receding gumline. You’re absolutely certain your smile looks more like a jack-o-lantern’s grimace than a genuine expression of warmth. You don’t need to clamp your mouth shut forever, but rather take a stab at a few methods that may help you regrow gums. Gum disease is the leading cause of extensive of gum damage. Feel fortunate that you found out the problem before you developed things like loose and sensitive teeth. If you already have sensitive or loose teeth, don’t waste any more time. Get yourself back to your dentist to get help with your receding gum problem. It’s always helpful to walk in with some knowledge of the receding gum treatments. Continue reading
How Neem Works
In the old days the people in India did not use neem toothpaste. They used neem toothbrushes instead. Chewing on a neem twig has for many centuries been the commonly preferred way to prevent gum disease and maintain healthy teeth. These rural people had never used a “real” toothbrush, didn’t know Crest or Colgate, yet they had perfect teeth. A perfect natural solution. Researchers believe the tradition of using neem twigs for dental care has helped Indian villagers to avoid cavities and tooth loss, although they have no access to modern dental care facilities or products. Continue reading
Questions and Answers : Gums
What are gums?
Gums are also known as gingival. They are part of oral tissues which support our teeth and cover the bone. Â 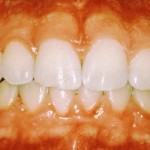 Continue reading
Continue reading
How to Prevent Gum Recession With a Tongue Piercing
If you have or want to get your tongue pierced, it is important to receive proper care to avoid infection and gum recession. Gum recession, or periodontitis, is a very common problem with tongue piercings due to the jewelry rubbing against the gums. This can eventually lead to exposed roots, which cause much pain and, eventually, loss of teeth.
When considering lip piercing, you should be aware of the risks that you may encounter while wearing lip ring. To avoid the most common risks of a lip ring piercing, book an appointment with a professional piercer to discuss your desire to get one. Ask about the healing process, and how you can avoid damage to your teeth and gums while wearing a lip ring. Continue reading
Laser Dental Cleaning
Lasers have been used in dentistry since 1994 to treat a number of dental problems. But, despite FDA approval, no laser system has received the American Dental Association’s (ADA) Seal of Acceptance. That seal assures dentists that the product or device meets ADA standards of safety and efficacy, among other things. The ADA, however, states that it is cautiously optimistic about the role of laser technology in the field of dentistry. These lasers are different from the cold lasers used in phototherapy for the relief of headaches, pain, and inflammation. Continue reading
Best Toothbrush for Periodontal Disease
Best toothbrush for periodontal disease
The importance of oral hygiene has been highlighted over the years and recently awareness has been created as it is not only for good dental health but one’s overall well-being. Gum disease is a major risk factor and has been associated with serious health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, strokes, respiratory disease, digestive disorders, pancreatic cancer and preterm low birth weight
babies. It begins with bacteria invading the gums and populating in great amounts destructing the tooth tissues and supporting tissues. If the early stage of gum disease (gingivitis) if left untreated, it can progress to more severe gum disease (periodontitis).
Periodontitis comes with swollen and bleeding gums, recession, tooth sensitivity, root decay, loose tooth leading to tooth loss in advanced cases. The best way for treating gum disease is by regular brushing and flossing. It is essential for one to administer proper brushing techniques with the right toothbrush for the health of their gums and prevent tooth loss as well as fighting against other health challenges. There are various types of toothbrushes available in the market, with newer products seems better than
previous ones. Hence, the confusion arises to select the best toothbrush to care for their teeth and gums. Continue reading