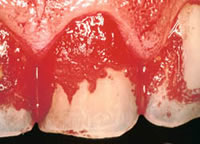
With these concepts in mind, let us review the histology of the periodontal pocket, especially in the area of tissue destruction and healing after the periodontal therapy instituted. The periodontal pocket is described as one which occurred with destruction of the supporting periodontal tissues. Progressive pocket deepening leads to destruction of the supporting periodontal tissues and loosening and exfoliation of the teeth. The suprabony pockets are those which the bottom of the pocket is coronal to the underlying alveolar bone. The infrabony pockets are those which the bottom of the pocket is apical to the level of the adjacent alveolar bone and the lateral pocket wall lies between the tooth surface and the alveolar bone. Continue reading
Category Archives: Periodontics
New attachment and reattachment Part 1
The goal of Periodontal therapy is to halt the disease progression and prevent its recurrence, and restore the lost periodontal structure which occured as the result of the disease destruction. The later goal prompts us to evaluate the concept of “new attachment†or “regenerationâ€, and “reattachment†or “repairâ€. Each concepts will lead to different mode of periodontal therapy, and ultimately different result. New attachment is the ideal, desired goal, which each periodontist today are trying to achieve in every possible way. Continue reading
Types of Scalers
The American Academy of Periodontology published a position in paper summarizing what is known about these instruments and how they compare in their effectiveness (J. Periodontol 2000:71;1792-1801). Recent modifications of tip design for power driven scalers provide improved access into deep pockets and difficult to reach areas such as furcations. Therefore, studies were undertaken to shed light on the potential roles of sonic and ultrasonic scalers in periodontal therapy. Continue reading
Surgical exposure of impacted tooth
When a tooth fails to emerge through the gums, it is considered to be an impacted tooth. This commonly occurs in the case of canine teeth.
It is important to treat an impacted tooth in order to prevent the improper eruption of nearby teeth, cyst formation, possible infection or other negative changes in the jaw. Continue reading
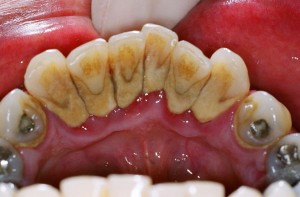
Is Dental Plaque the Main Cause of Dental Caries?
Our mouth is constantly bathed in saliva and is exposed to the passage of food, the oral flora and many other stimuli considering the variety of objects that people put in their mouths such as cigarettes, pipes, hair-grips and so on. Nevertheless, our mouth has a remarkable ability to resist and adapt according to these stimulations. Our teeth are also exposed to the same factors and they can be covered wholly or in part by food debris, soft and hard deposits.
Â
Dental Plaque, the main cause of Dental Caries
Dental Plaque is a soft but adherent deposit of bacteria and their products, which forms on all tooth surfaces and other objects in the mouth, for example; fillings or dentures. This Plaque formation is a natural, physiological process and is an example of a biofilm, which means it is not a haphazard collection of bacteria but a complex association of many different bacterial species living together in a single environment. For instance, a newborn baby’s mouth is sterile but within a few hours, microorganisms appear; mainly Streptococcus salivarius. By the time the baby had his/ her first tooth out, a complex flora is established.
Â
Basically, Dental Plaque is scarcely visible in thin layers and it can be revealed only by the use of a Plaque-Disclosing Agent. In thick layers, it can be seen as yellowish or grey deposits which cannot be removed with mouthwashes or by irrigation but can be brushed off. It is usual to find it on areas which are difficult to reach by tooth brushing, for example; in between teeth or in severely crowded teeth. When Dental Plaque calcified or mineralized, it will become Dental Calculus or commonly known as Tartar. It is a ‘stony crust’ that forms on teeth and has long been associated with Gums Disease. Having said that; Dental Plaque is the main cause of dental caries.
Â
Â
     Â
Â
Â
Â
      Â
    Â
Â
Â
Â
Continue reading
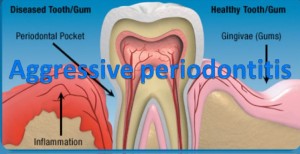
Aggressive periodontitis
Gum disease is not limited to adults. Periodontitis (inflammation of the supporting tissues of the teeth or also known as the periodontium) can also occur in young people. Periodontal disease can generally be divided into different types including chronic, aggressive and necrotizing periodontal disease; with aggressive periodontitis commonly seen in the younger age group. Continue reading
What is dental splinting?
Dental splinting is the joining of two or more teeth into a rigid unit by means of fixed or removable restorations/devices. A periodontal splint is an appliance used for maintaining or stabilizing mobile teeth in their functional position. The main objective of splinting is to promote healing and to increase the patients comfort and function.