Spaced dentition is characterized by interdental spaces and lack of contact points between the teeth. Spacing can be localized or generalized due to the number of teeth included. It is a common esthetic problem for many patients. A study in European adults showed that patients with broad midline spacing were perceived as being less socially successful and having lower intelligence. Continue reading
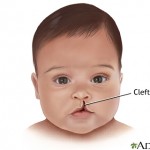
Cleft lip and palate (part 1)
Cleft lip and cleft palate are birth defects affecting the mid facial region. Patients with cleft lip might have a small notch on the lip or a wide opening which involves the lip and the palate ( the roof of your mouth) The exact cause of cleft lip/palate is unknown but it is believed that genetic, usage of certain drugs during pregnancy, viruses, toxins are the causative factors of cleft lip and palate. Continue reading
Crossbite
Crossbite is an occlusal irregularity where a tooth (or teeth) has a more buccal or lingual position (that is, the tooth is either closer to the cheek or to the tongue) than its corresponding antagonist tooth in the upper or lower arcade. Continue reading
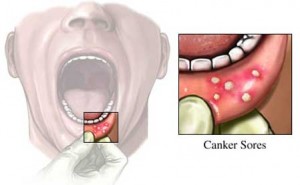
Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) Part 2
Continued from Part 1
How is recurrent aphthous stomatitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of recurrent aphthous stomatitis is based on the history and clinical features, as no specific tests are available. Biopsy is rarely indicted and is only usually needed where a different diagnosis is suspected. However to exclude the systemic disorders, it is useful to undertake investigations on blood (for example full blood picture) and serum (for example ferritin levels and vitamin B12 measurements). Continue reading
Dental anomalies among children
 1)Â Â Â Â Â HYPODONTIA :
1)Â Â Â Â Â HYPODONTIA :
A dental condition where by the patient has missing teeth as a result of their failure of development. The most common missing tooth is the third molars, or known as wisdom tooth.  Hypodontia can be due to genetic or environmental factors.  It is been reported in association with low birth weight, increased maternal age and etc. Continue reading
Trial denture try in Part 3
Denture base extension:
The lower trial denture extension should be tested with the patient mouth is opened no more than half opened position. To allow the surrounding musculature is in an acceptable state of relaxation.
• Labial and buccal extensions are checked as for the upper trial denture. Continue reading
Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) Part 1
Although a variety of mouth ulcers may recur, for example those associated with mechanical trauma and skin disease; there is a group of ulcers that arise due to unknown causes whose natural history is characterized by frequent recurrences over a number of years. It is to this group that the collective term recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS) is applied. Continue reading
Chrome cobalt dentures – Q & A
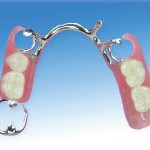 What is chrome cobalt denture?
What is chrome cobalt denture?
Chrome cobalt dentures are dentures made from cast cobalt chrome framework/base. They are made of a type of allow which consists of cobalt, chrome, chromium (which is added to prevent corrosion). Continue reading
Trial denture try in Part 2
Denture base extension:
a) The labial and buccal extension:
- If marked overextension of the flanges, will stretch the sulcus tissues when denture inserted, leading to elastic recoil result in dislodgment of the denture, immediate denture displacement after its seating.
Continue reading
Trial denture try in Part 1
Definition:
Preliminary insertion of complete denture wax up (trial denture) to determine the fit, esthetics, maxillomandibular relations —–etc.