If you’re searching for an OraMD Review or OraMD Reviews – then the chances are you’re trying to get a cure for bad breath and/or gum disorders. It’s no secret that your dentist’s solution (fluoride toothpaste) simply doesn’t work. If it did – you wouldn’t be looking for a review of OraMD. For years we’ve all been completely misled by the toothpaste makers. So – if you’re going to brush your teeth twice a day – better make sure you’re using a natural product that will do the job. Continue reading
Effect of Systemic Factors on the Periodontium Part 2
Continued from Part 1
Drug reactions
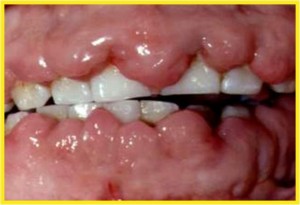
- Epanutin/phenytoin/dilantin/DPH – an anticonvulsant drug given to epileptics, some degree of gums enlargement occurs in a large percentage of epileptics taking phenytoin, especially in those under 40 years of age.
- Cyclosporine – an immunosuppressive drug, it can produce fibrous hyperplasia of the gums. The condition is however less common in patients on cyclosporine, but when it occurs it may be very severe.
- Nifedipine – a calcium channel blocking drug given to treat cardiac angina, arrhythmias and hypertension, it produces fibrous hyperplasia of the gums. Nifedipine hyperplasia is less firm than the other two, and contains a higher proportion of ground substance. Continue reading
Effect of Systemic Factors on the Periodontium Part 1
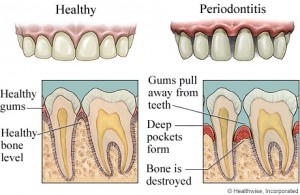
The periodontium or the commonly known as the tooth supporting tissues consists of the gums, alveolar or jaw bone, the periodontal ligament and the cementum of tooth. Numerous systemic conditions can have effects on the periodontal tissues such as:
- Physiological changes (mainly sex hormone effects)
- Systemic disease – endocrines, genetic conditions, granulomatous conditions, blood disorders, immunological conditions, dermatoses
- Infections
- Drug reactions
- Dietary and nutritional factors
This article will discuss some of the systemic factors stated above that are more commonly seen. Continue reading
Cap splint
Pediatric mandibular fractures are not commonly encountered. The elasticity of bones in a child prevents loss of continuity of bone and rather results in a bending of a cortex termed as a greenstick fracture. Occlusion is rarely a problem as there is no disruption or mild changes are remodeled during the development of permanent dentition. In case of a severely displaced fracture the treatment option can vary from intermaxillary fixation, cap splints to plating with mini plates or resorbable plates. Continue reading
An Approach to Oral Ulcers
Oral ulceration is probably the commonest oral mucosal disease seen and it may also be the most serious. It is important therefore not to underestimate that ulcer in your mouth, especially if it persists for a long time. Continue reading
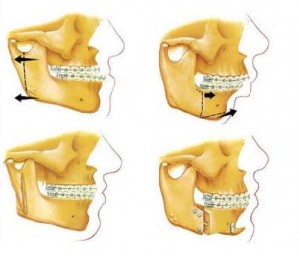
Orthognathic Surgery: What Is It?
Sometimes surgical procedures might be needed during orthodontic treatment when malocclusion is severe and beyond the limits of treatment with fixed dental braces. This orthodontic surgery procedure is called orthognathic surgery. Continue reading
Dental pins
When the teeth are decayed and it has to be restored the dentist goes for the filling but sometimes the decay is extensive and a large part of the tooth is lost. In such cases pins and posts are used as the simple filling material can not give the adequate strength to sustain the masticatory forces and fractures. The pins and posts can be used separately or together as decided by the dentist. Continue reading
Getting Adult Braces
There has been an increase in adults seeking orthodontic treatment over the recent years and it can be due to various reasons that include:
- Improved dental awareness with the advent of preventive dentistry and teeth are retained longer in the mouth.
- The issue of esthetic concern has reduced due to the introduction of ceramic and lingual brackets.
- Orthodontics or the wearing of teeth braces is now socially acceptable and can be a sign of affluence.
- Recommended by general dentists for restorative and periodontal care.
- Insurance and claims for dental treatment in some countries. Continue reading
Caries diagnosis Part 3
Although the evidence shows that many diagnostic methods are less than desirably accurate, current diagnostic interpretations still must be used until new, more sensitive, techniques are available and validated. The evidence-based reports supported previous caries experience and pathologically low salivary flow rate as indicators of significant risk. Most studies from the systematic reviews involved children and excluded root caries, adults, and anterior teeth. Therefore, the clinician must extrapolate reportedly successful preventive and arresting/remineralization techniques from children to adults, root caries, and anterior teeth. In the absence of clear evidence on adequately sensitive diagnostic methods for detecting early noncavitated lesions and risk assessment indicators, clinicians need guidelines for treatment. Continue reading
Caries diagnosis Part 2
Numerous risk indicators, that is, characteristics or measurements that assist in the prediction of caries, whether or not they are involved in caries causation, have been suggested for children. Unfortunately, more of the supportive data come from cross-sectional correlations with accumulated caries experience than from prospective, protocol-based incidence studies. The prospective studies employed different combinations of potential predictors in a variety of populations, varied considerably in sample size and quality, and have not produced a broadly applicable index or set of criteria for risk assessment. More and higher-quality comprehensive, longitudinal, multifactor studies of implicated risk indicators are needed to obtain firm support for their associations with caries incidence, to clarify the strengths of these associations in differing populations, and to reveal the extent to which the risk indicators provide independent as opposed to redundant information. In addition, although the nature of the disease process suggests that many of the proposed indicators may well be appropriate throughout life, validation studies in adult populations are largely absent or incomplete. Continue reading