Continued from Part 1
First aid advice for parent or caregivers
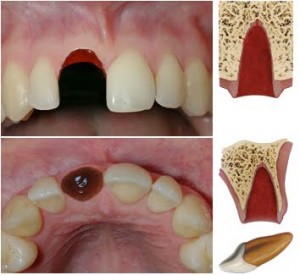
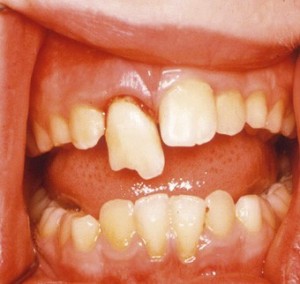
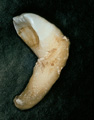
Always check the child’s clothing for avulsed teeth that are thought to be lost. It is important that parents, caregivers and teachers have assess to appropriate advice on the management of avulsed teeth. Timing is essential and this information can be given over the telephone. Continue reading