What is a dry socket?
What is a dry socket?
Dry socket or also known as alveolar osteitis is a common complication occurring after the extraction of a permanent teeth especially the lower wisdom teeth. The term ‘alveolar’ refers to the jawbone that supports teeth while ‘osteitis’ refers to the inflammation of the bone associated with the extraction socket.
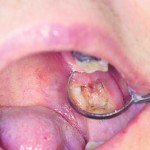
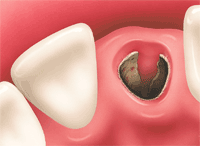
The condition has generally been characterized by degraded or delayed healing associated with breakdown or dislodgement of the blood clot in the extraction socket. It is usually accompanied by persistent, radiating pain in and around the extraction site within a few days after extraction that is not easily relieved by pain killers. The premature loss or breakdown of the blood clot is accompanied by exposure of the underlying bone. Continue reading