Sore tongue medically known as stomatitis is a very common symptom. Most of the doctors routinely prescribe B-complex tablets, terming it B-complex deficiency. In fact in many instances it is not so. Painful tongue is a common problem. Many of us experience a sore tongue from time to time. But what should you do about it if it affects you. Continue reading
Tag Archives: oral cancer
Biopsy: What to Expect
Sometimes you may hear the term ‘biopsy’ when investigations are required for certain lesions in the mouth. Biopsy sounds like a scary procedure that brings the word ‘cancer’ to mind but in fact it is just an aid for diagnostic purposes. Continue reading
Oral Cancer: Treatment Options and Complications
Continued from Part 4
What are the principles of treatment for oral cancer?
Individuals with oral cancer often present too late for cure and some may not benefit from treatment. Three treatment options are possible:
- Attempted cure
- Active palliative care
- Supportive care only pending death
If cure is attempted, the highest chances of success are given by multimodality treatment – a combination of surgery, radiotherapy, and more rarely, chemotherapy. The most aggressive treatment that the individual is able to withstand will be recommended because if the first round of treatment fails, the chances of survival are much reduced. Continue reading
Oral Cancer: Investigations and Staging
Continued from Part 3
What are the investigations needed for oral cancer?
Investigations are done to see the extent of cancer and to confirm the diagnosis. The following investigations may be indicated:
- Jaw radiography or x-ray
- Chest x-ray or computed tomography (CT). This is important as a pre-anesthetic check especially in individuals with known airways disease, and to demonstrate second primary tumors or spread to lungs or lymph nodes, ribs or vertebrae.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or CT of the primary site, of the head and neck, and suspected sites of distant spread. MRI is particularly useful to determine tumor spread, soft tissue involvement and lymph nodes involvement.
- Electrocardiography
- Blood test: full blood picture and hemoglobin, blood for grouping and cross-matching, urea and electrolytes, and liver function tests.
- Biopsy. Biopsy is a tissue sample taken for histopathological analysis and it gives confirmative diagnosis. Continue reading
Oral Cancer: Risk Factors Part 3 and Symptoms
Continued from Part 2
Chronic infections
Chronic candidal infection
This is often associated with speckled leukoplakias and such lesions are particularly prone to undergo cancerous transformation, though the role of candidal or yeast infection in malignant transformation must be regarded as uncertain. Continue reading
Oral Cancer: Risk Factors Part 2
Continued from Part 1
Betel quid (paan) and other chewing habits
Paan chewing is one of the most widespread habits in the world and is practiced by over 200 million people worldwide. It is particularly common in South-East Asia and the Indian subcontinent and is also prevalent within these ethnic communities in parts of the USA. The composition of the quid varies but basically consists of betel nut and slaked lime wrapped in a betel leaf to which tobacco and various spices are often added. The quid is usually placed in the cheek pockets and is frequently kept in the mouth for a long time. As the quid is chewed, alkaloids are released from the nut and the tobacco which are said to aid digestion and to produce a slight euphoric effect. The habit is more common in women than in men, and although the frequency of use increases with age the habit often starts in childhood. Continue reading
Oral Cancer: Facts and Risk Factors Part 1
Oral cancer is the sixth most common cancer reported worldwide. Oral cancer affects twice as many men as in women. For every 100,000 people, 6.3 males and 3.2 females are likely to develop mouth cancer. However this difference is less than it has been in the past, partly due to changes in smoking habits. Continue reading
Oral Submucous Fibrosis
Oral submucous fibrosis (or OSF) is a chronic, complex, irreversible, highly potent pre-cancerous condition characterized by juxta-epithelial inflammatory reaction and progressive fibrosis of the submucosal tissues (lamina propria and deeper connective tissues). As the disease progresses, the jaws become rigid to the point that the sufferer is unable to open his mouth. The condition is linked to oral cancers and is associated with areca nut chewing, the main component of betel quid. Areca nut or betel quid chewing, a habit similar to tobacco chewing, is practiced predominately in Southeast Asia and India, dating back thousands of years. Continue reading
Oral cancer
Introduction
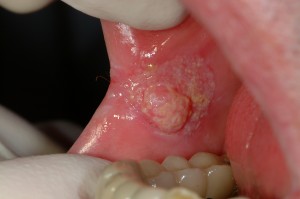
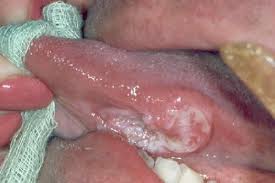
Oral or mouth cancers are any tumours that grows anywhere in the mouth. They are often associated with tobacco use. It is a condition of concern because some oral cancers are fatal if not detected and treated early, such as squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), which is due to uncontrolled proliferation of the squamous cells. Almost all oral cancers begin in the flat cells (squamous cell) that cover the surfaces of the mouth, tongue, and lips.
Oral Health: Relationship between the body and mouth II
Continue from section I…
Is there a way to link oral signs and symptoms to certain diseases?
In some diseases, there can be very specific oral health presentations or manifestations. In fact, there are times where the mouth is the first site to show signs of an underlying systemic condition, preceding clinical diagnosis by months. Hence it is important that if you noticed any sudden changes in your mouth that cannot be relate back or correspond to a known cause, it may be wise to monitor those changes. If the abnormal changes persist for weeks or become symptomatic, it is best to get it checked out by a dentist as soon as possible to prevent late diagnosis and complications.
Below is an outline of possible oral health problems or presentations under some of the common conditions or diseases of the body: Continue reading