Our mouth is constantly bathed in saliva and is exposed to the passage of food, the oral flora and many other stimuli considering the variety of objects that people put in their mouths such as cigarettes, pipes, hair-grips and so on. Nevertheless, our mouth has a remarkable ability to resist and adapt according to these stimulations. Our teeth are also exposed to the same factors and they can be covered wholly or in part by food debris, soft and hard deposits.
Â
Dental Plaque, the main cause of Dental Caries
Dental Plaque is a soft but adherent deposit of bacteria and their products, which forms on all tooth surfaces and other objects in the mouth, for example; fillings or dentures. This Plaque formation is a natural, physiological process and is an example of a biofilm, which means it is not a haphazard collection of bacteria but a complex association of many different bacterial species living together in a single environment. For instance, a newborn baby’s mouth is sterile but within a few hours, microorganisms appear; mainly Streptococcus salivarius. By the time the baby had his/ her first tooth out, a complex flora is established.
Â
Basically, Dental Plaque is scarcely visible in thin layers and it can be revealed only by the use of a Plaque-Disclosing Agent. In thick layers, it can be seen as yellowish or grey deposits which cannot be removed with mouthwashes or by irrigation but can be brushed off. It is usual to find it on areas which are difficult to reach by tooth brushing, for example; in between teeth or in severely crowded teeth. When Dental Plaque calcified or mineralized, it will become Dental Calculus or commonly known as Tartar. It is a ‘stony crust’ that forms on teeth and has long been associated with Gums Disease. Having said that; Dental Plaque is the main cause of dental caries.
Â
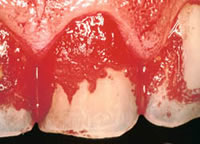
Dental plaque (in red) visible through plaque disclosing agent
Â
     Â
Â
Â
Â
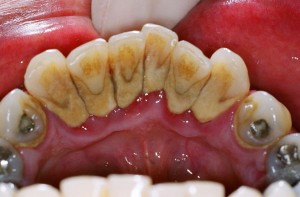
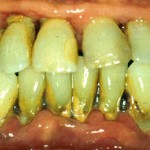
Dental calculus/ tartar
      Â
    Â
Â
Â
Â
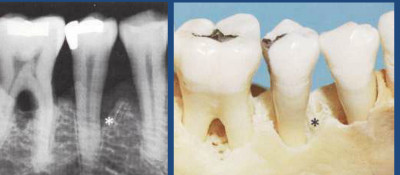
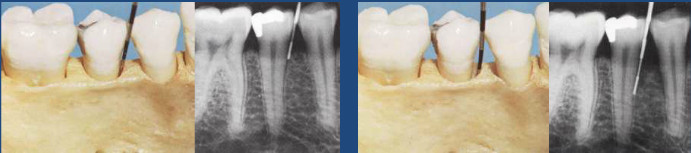 Careful radiographic or x-ray examination is done but it may not reveal the presence of a bone defect or its precise morphology.
Careful radiographic or x-ray examination is done but it may not reveal the presence of a bone defect or its precise morphology.