Pediatric mandibular fractures are not commonly encountered. The elasticity of bones in a child prevents loss of continuity of bone and rather results in a bending of a cortex termed as a greenstick fracture. Occlusion is rarely a problem as there is no disruption or mild changes are remodeled during the development of permanent dentition. In case of a severely displaced fracture the treatment option can vary from intermaxillary fixation, cap splints to plating with mini plates or resorbable plates. Continue reading
Tag Archives: permanent teeth
Extraction of baby teeth
1. Why extract a baby tooth?
Choosing between extraction and filling or conservation is a very common decision that both dentists and patients have to take every day. With adults the decision making is much easier, if the tooth is restorable and the patient can pay for the treatment then we simply conserve the tooth. If the patient is a child then the process of decision making is much harder as many factors affect the selection of the treatment plan that the dentist have to follow. Continue reading
Dental care for osteogenesis imperfecta patients Part 2
General Care for People With OI Plus DI
Children with OI and dentinogenesis imperfecta need the same basic care as discussed in Part 1, but they also need to be monitored for cracking, chipping and abrasion of the teeth. Special care will be needed even with the baby teeth. All of the teeth may not be affected by DI, and primary teeth usually are affected to a greater extent than the permanent teeth. Restorative treatment may be needed at some point. Continue reading
Dental care for osteogenesis imperfecta patients Part 1
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is always associated with bone fragility. In addition, OI may affect the growth of the jaws and may or may not affect the teeth. About half of the people who have OI have teeth that appear normal, and their major concerns are routine care. However, the other half has a defect in the teeth called dentinogenesis imperfecta (DI), sometimes referred to as opalescent teeth or brittle teeth. These teeth may be misshapen, may chip or break easily, and will require special care. Continue reading
Eruption dates
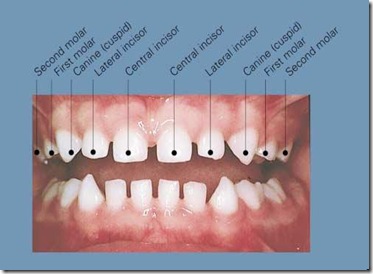
Human beings have two sets of teeth —- Primary (milk teeth) and Permanent. There are 20 primary and 32 permanent teeth. In some people one or more teeth may be absent, or they may have some extra teeth (supernumerary). Usually the first primary teeth erupt by 6 months and the first permanent by 6 years of age. Children loose their milk teeth between 6 and 11 years of age. By the age of 13 years almost all the permanent teeth have erupted: 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars and 12 molars. The last 4 molars commonly known as wisdom teeth appear much later, between 18 to 21 years. The main function of your teeth is to chew and cut food. Anterior teeth are used to bite and tear food while the posterior teeth help in chewing. Hence your dental health is an important part of your general health and your overall well-being. Continue reading
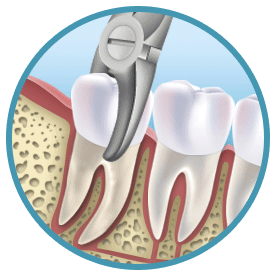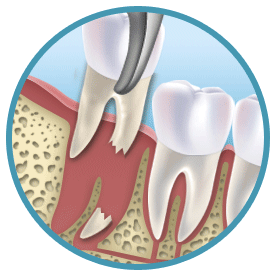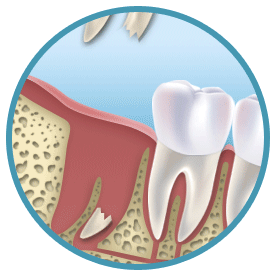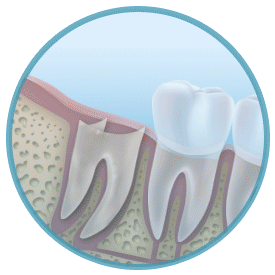
Teeth Extraction Techniques
Tooth extraction may sound easy but in fact experiences as well as the proper teeth extraction techniques are required to ensure that the tooth is safely out of the mouth. There are generally two methods of teeth extraction – simple or surgical extraction. Continue reading
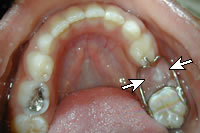
Space Maintenance in Children
Â
Â
Space Maintainer is a fixed or removable appliance designed to preserve the space created by the premature loss of a tooth (can be primary or permanent tooth). Fixed Space Maintainer is not intended to be removed by the patient whereas Removable Space Maintainer is designed for easy removal for cleansing and/or adjustment. Continue reading
How to Root Canal a Baby Teeth
The purpose of root canal treatment with baby teeth is to keep the teeth in function until exfoliation, or at least for as long as they are important for occlusal development. Besides eating and speaking, many parents do not know that baby teeth (or primary teeth) also act as a guide for the underlying permanent teeth to erupt and at the same time they maintain the space on the arch so that the permanent teeth has enough room to grow when it is out. Continue reading
Two sets of teeth in our lifetime
We have two sets of teeth in our lifetime.
The first set of our teeth is known as deciduous/primary/milk/baby/temporary teeth. There are a total of 20 teeth in the oral cavity/mouth.
On the upper jaw, there are 2 central incisors, 2 lateral incisors, 2 canines and 4 molars making it a total of 10 teeth. Same goes for the lower jaw making it a grand total of 20 teeth altogether. Continue reading
Tips for Extraction of Baby Teeth
All people at some point in their lives will need to have their baby teeth extracted. The primary reason for extracting these teeth is to make room for permanent teeth. Other reasons for extraction are to prevent the crowding of teeth in the mouth, circumvent tooth decay or prevent injury to the inside of the jaw. No matter which of these scenarios describes your circumstances, there are a number of ways to safely extract baby teeth. Continue reading