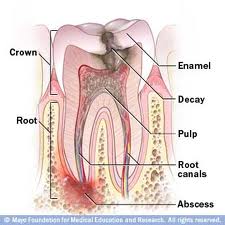
 Having a tooth abscess is literally a pain therefore one would not have second thoughts in pulling the miserable tooth out. However tooth extraction may not be the only way out of the pain. Continue reading
Having a tooth abscess is literally a pain therefore one would not have second thoughts in pulling the miserable tooth out. However tooth extraction may not be the only way out of the pain. Continue reading
Tag Archives: root canal therapy
What Happens at an Appointment with an Endodontist? Part 2
Continued from Part 1
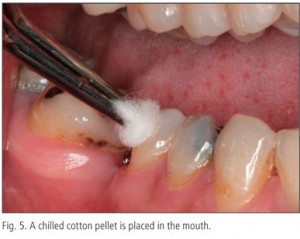
Cold testing
A cold stimulus such as refrigerant spray is sprayed on a cotton pledget and applied to the tooth under investigation.
Heat testing
A heated source such as a GP stick is applied to the tooth. Continue reading
What Happens at an Appointment with an Endodontist? Part 1
Your dentist referred you to an endodontist for a root canal treatment that he/she finds difficult to do. However you started having the jitters about your endodontic appointment since this is a specialist you are seeking. This article will give you a gist on what happens at an appointment with an endodontist. Continue reading
Success Rate and Outcomes of Root Canal Therapy
 Every stakeholder in dental delivery system has different definitions and expectations regarding the outcome and result of root canal treatment. As a patient, you might be concerned about the function and esthetic of the endodontically treated tooth where as your dentist will judge the outcome of a root canal treatment based on the results of clinical and radiographic examinations. Continue reading
Every stakeholder in dental delivery system has different definitions and expectations regarding the outcome and result of root canal treatment. As a patient, you might be concerned about the function and esthetic of the endodontically treated tooth where as your dentist will judge the outcome of a root canal treatment based on the results of clinical and radiographic examinations. Continue reading
What is Endodontics?
 What is Endodontics?
What is Endodontics?
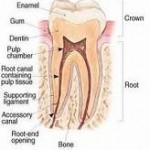
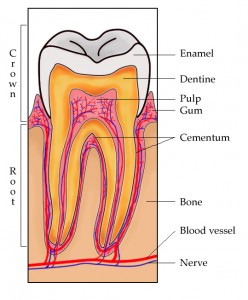
Endodontics is the diagnosis and treatment of inflamed and damaged pulps. Teeth are made up of protective hard covering (enamel, dentin and cementum) encasing a soft tissue living tissue called pulp.
Pulp c0ntains blood vessels, nerves, fibers and connective tissue. The pulp extends from the crown of the tooth to the tip of the roots where it connects to the tissues surrounding the root. The pulp is important during a tooth’s growth and developement. However, once a tooth is fully mature it can survive without the pulp, because the tooth continues to be nourished by the tissues surrounding it.
Dental Root Canal Procedures
 What do you expect when your dentist tells you that you have to undergo root canal treatment in order to save your tooth? Read here to find out when do you need root canal treatment. Continue reading
What do you expect when your dentist tells you that you have to undergo root canal treatment in order to save your tooth? Read here to find out when do you need root canal treatment. Continue reading
What Is the Purpose of a Root Canal Treatment?
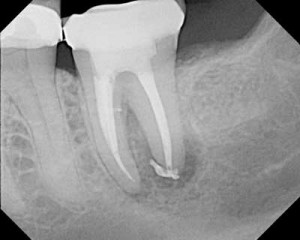
A root canal treatment (RCT) is a procedure whereby the pulp of the tooth is extirpated, and filled with suitable filling materials to replace the pulp. It is also known as endodontic therapy, and the sole purpose for endodontic therapy is to remove all the inflamed and necrotic tissues in the pulp, as well as the bacterial component, making the pulp and the root canals of the tooth as clean as possible. Continue reading
Root Canal Treatment- How is it performed?
A tooth consists of enamel, dentine, cementum and pulp. The pulp is a living tissue, inhabitated by nerve tissues, blood vessels and cells responsible for tooth formation and repair. Root canal therapy /treatment (endodontic therapy) involves removal of these structure which have been contaminated by bacteria and damaged permanently. The subsequent hollow space is cleaned, shaped and decontaminated using files and irrigants. The decontaminated space is then filled with inert filling material. After root canal therapy, the tooth will be ‘dead’ or non vital because it contains no living tissues. Continue reading
How to Tell If a Root Canal Needs to be Redone?
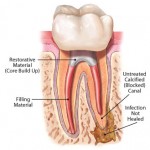 What is Root Canal Retreatment?
What is Root Canal Retreatment?
Root canal retreatment, also known as endodontic nonsurgical retreatment is a procedure that is carried out on a tooth that previously had root canal treatment. Because of the complexity of the procedure, it is usually done by an endodontist. There are several reasons why a previously root canal treated tooth can fail. Continue reading
The Dangers of Root Canal Treatment
Endodontic treatment, which is often referred to as root canal treatment (RCT), root canal procedure or root canal therapy, involves pulp and root canal removal as well as cleaning and filling of the resultant space, in order to prevent microorganisms from multiplying within the root canal system and spreading to the gum tissues. Like any dental procedure, there can be hits and misses with root canal treatment. There is no guarantee that every root canal treatment case would have 100% success for there may be certain factors beyond the dentist’s control or it might be just plain human error. Continue reading