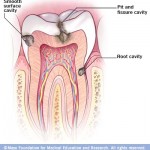
Acid erosion, also known as dental erosion, is the irreversible loss of tooth structure due to chemical dissolution by acids not of bacterial origin. Dental erosion is the most common chronic disease of children ages 5–17, although it is only relatively recently that it has been recognised as a dental health problem. There is generally widespread ignorance of the damaging effects of acid erosion; this is particularly the case with erosion due to fruit juices, because they tend to be seen as healthy. Erosion is found initially in the enamel and, if unchecked, may proceed to the underlying dentin. Continue reading
Tag Archives: saliva
Kaposi’s sarcoma Part 2
Mouth
Is involved in about 30%, and is the initial site in 15% of AIDS-related KS. In the mouth, the hard palate is most frequently affected, followed by the gums. Lesions in the mouth may be easily damaged by chewing and bleed or suffer secondary infection, and even interfere with eating or speaking. Continue reading
Having Too Much or Too Little Saliva Part 1
Saliva is essential to oral health and individuals who have too much or too little saliva can affect many functions, and may develop infections as a consequence of the reduced defenses. Continue reading
Types of papillae on tongue
Taste buds contain the receptors for taste. They are located around the small structures on the upper surface of the tongue, soft palate, upper esophagus and epiglottis, which are called papillae. These structures are involved in detecting the five (known) elements of taste perception: salty, sour, bitter, sweet, and umami. Via small openings in the tongue epithelium, called taste pores, parts of the food dissolved in saliva come into contact with taste receptors. These are located on top of the taste receptor cells that constitute the taste buds. The taste receptor cells send information detected by clusters of various receptors and ion channels to the gustatory areas of the brain via the seventh, ninth and tenth cranial nerves. Continue reading
How to Clean and Reduce Plaque With Saliva
Saliva is a complex fluid found in the mouth consisting of a mixture of secretions from the major salivary glands and the minor glands of the tissues in the mouth. Majority of saliva is produced by the three pairs of major glands – the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. The rest of it is produced by thousands of minor salivary glands distributed throughout the mouth and throat. Continue reading
What to Eat After Having My Teeth Extracted
Before any tooth extraction, anesthesia will be given to the patient by the dentist to numb the area. The anesthesia usually lasts for a few hours, depending on what type of anesthesia the patient is given. Because of this, it is important for the patient to avoid hot food because the patient will not feel the burn if the food is too hot. For the same reason, the patient is also not allowed to take hard, chewy food, because the patient will not realize it even when he/she accidentally bites on his/her own lips or other soft tissues. Continue reading
Your Guide To Preventing Cavities
Â
Â
Dental decay is also known as cavities, and they occur when there is dissolution of the teeth surfaces. Our teeth is made up of crystal apatite, and they are very vulnerable to acid which will dissolve them. This organic acid is produced by bacteria found inside our mouth, and they derive the acid from food debris that are left inside our mouth. The three important factors that produce dental decay are bacteria, fermentable carbohydrate, and teeth. Therefore, to prevent formation of dental decay, one of the three factors must not be present in our mouth, as without one of it, formation of the organic acid will be impossible. Continue reading
Oral Health Pt 3: Importance of saliva
Continued from Pt 2…
Saliva is an integral part of oral health and many people do not actually realise the importance of saliva has in our mouth. The role of saliva is often underplayed due to lack of awareness. Saliva has many important functions and it is unfortunate that most people would only realise this when they have a chronic case of xerostomia or dry mouth, which is often hard to manage as treatment available involves mainly palliative care rather than a cure.
Function of saliva
There are three major salivary glands found in the mouth, along with many more minor ones. Each of the major salivary glands produces slightly different quality of secretion, some being more watery and others with a thicker consistency. All these secretions are combined together in the mouth to form saliva. Saliva consists of mainly water (95%), enzymes, salivary proteins and ions. Continue reading